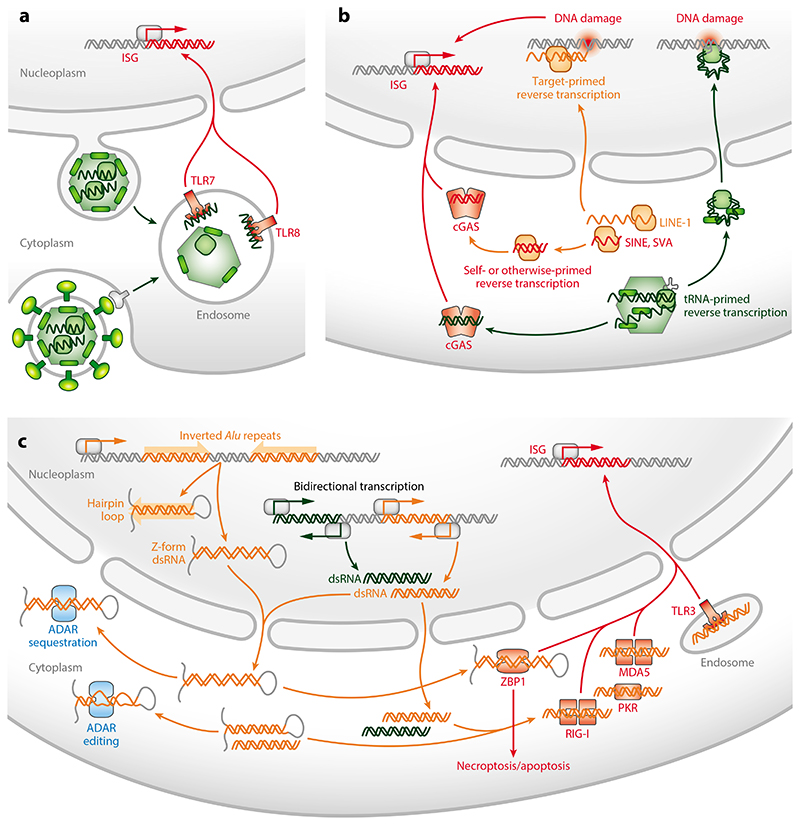
Figure 2.
Immunogenicity of canonical and aberrant ERE nucleic acid replication intermediates. (a) Endosomal sensors of ssRNA, TLR7, and TLR8 may be triggered by ERV genomic RNA. This can derive from incoming extracellular virus particles accessing the endosome after cell entry or from intracellularly formed particles gaining access to the endosome through alternative routes, including autophagy (not depicted). Not depicted is the signaling cascade initiated by TLR7 and TLR8 ligation, which ultimately leads to the transcriptional induction of ISGs. (b) Cytoplasmic DNA sensors such as cGAS may be triggered by cDNA produced by ERVs, as part of the typical ERV replication cycle, or by non-LTR retroelements through aberrant cytoplasmic reverse transcription. The latter can be self-primed (as in the case of Alu) or primed by an as yet unknown mechanism. Triggering of cGAS and its downstream adaptor STING (not depicted) then leads to an ISG response. Separately, the endonuclease activities of ERV polymerase and LINE-1 ORF2p catalyze DNA breaks during the replication cycle, and the ensuing DNA damage may indirectly trigger an ISG response. (c) Potentially immunogenic dsRNA is also aberrantly produced by LTR and non-LTR retroelements through distinct mechanisms. Bidirectional transcription of EREs generates intermolecular complementary RNA, forming dsRNA. Transcription of inverted SINE/Alu repeats generates regions of intramolecular complementarity leading to the formation of hairpin loops. More enigmatic is the formation of Z-form dsRNA, also enriched for SINE/Alu sequences. The immunogenicity of hairpin loop and Z-form dsRNA may be reduced by ADAR-mediated editing and sequestration, respectively, but increased dsRNA formation or insufficient ADAR activity permits the triggering of several dsRNA sensors, including MDA5, RIG-I, PKR, and TLR3, initiating signaling cascades that converge to an ISG response. The Z-form dsRNA-binding protein ZPB1, which typically induces necroptosis or apoptosis, also contributes to the ISG response triggered when ADAR activity is reduced. Abbreviations: cDNA, complementary DNA; dsRNA, double-stranded RNA; ERE, endogenous retroelement; ERV, endogenous retrovirus; ISG, interferon-stimulated gene; LINE-1, long interspersed nuclear elements 1; LTR, long terminal repeat; SINE, short interspersed nuclear element; ssRNA, single-stranded RNA; SVA, SINE-VNTR-Alu; TLR, Toll-like receptor; VNTR, variable-number tandem repeat.