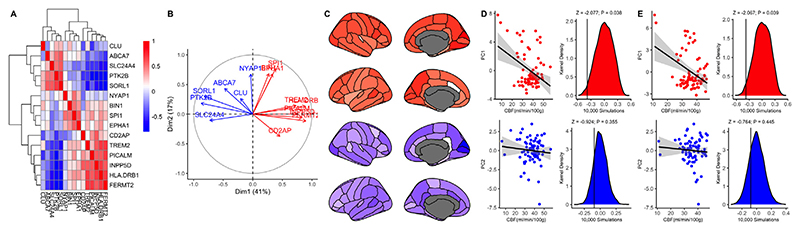
Fig. 4.
(A) Correlation matrix showing expression of AD risk genes. (B) Principal component analysis identified two principal modes of covariation between expression of all AD risk genes across the brain. (C) PC1-2 mapped onto the cortical regions. (D-E). Scatter plots show relationship between regional AD gene expression for PC1 (upper) and PC2 (lower) and regional CBF for the (D) Cardiff sample and (E) the ADNI sample. (D-E) Density plots for the distribution of 10,000 randomly simulated regional values (scaled to CBF range) for PC1-2 for Cardiff (D) and ADNI (E) samples. Solid black vertical lines represent the actual, observed correlation between PC1/2 AD gene expression and regional CBF.