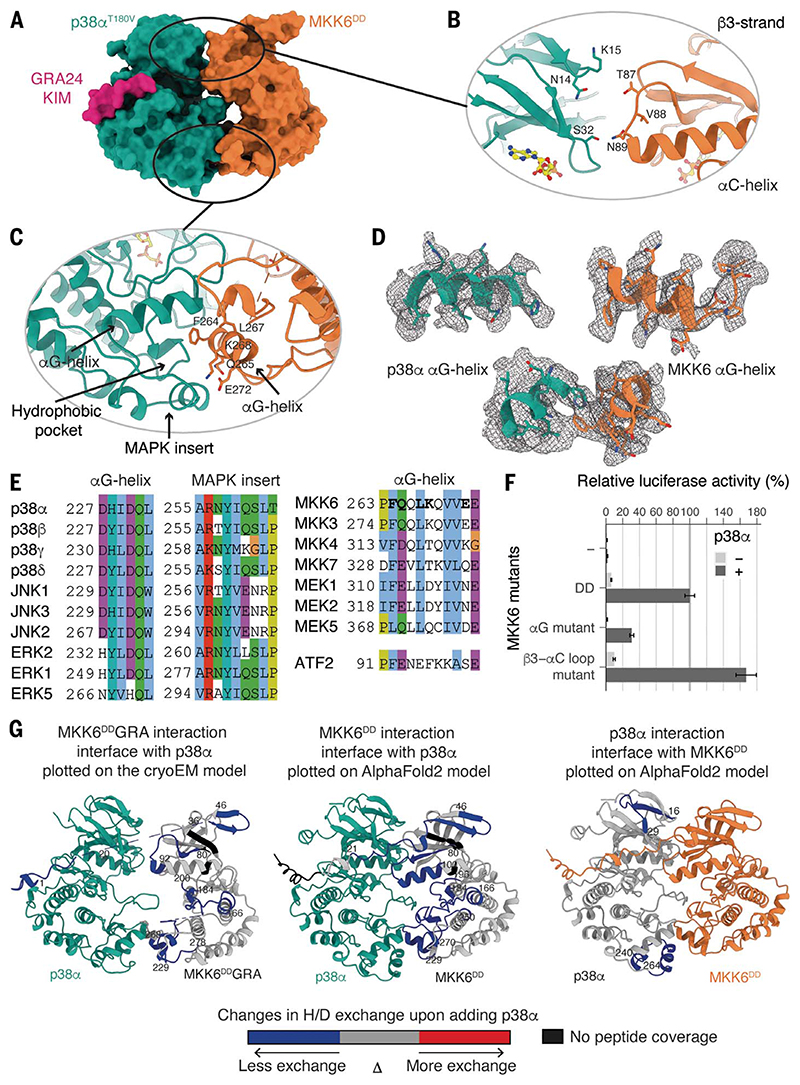
Fig. 2. Interaction interfaces between MKK6 and p38α, distal from the active site.
(A) Surface representation of the MKK6DDGRA-p38αT180V complex. (B) Potential interaction between the N lobes. (C) Interaction between the αG helix of MKK6 and the hydrophobic pocket of p38α. (D) αG helices of p38α and MKK6 in the sharpened Coulomb potential map (black mesh). (E) Sequence alignment of MAPK hydrophobic pockets, MAP2K αG helices, and the p38α substrate ATF2 peptide (Clustal coloring scheme). (F) Luciferase reporter assay to monitor the activity of the p38α signaling pathway in HEK293T cells, showing the ability of MKK6DD mutants to activate p38α (statistical analysis in table S6 and protein expression levels in fig. S10). (G) (Left) MKK6DDGRA and (middle) MKK6DD interaction sites with p38α and (right) p38α interaction sites with MKK6DD, identified with HDX-MS. Regions showing protection upon the addition of p38α or MKK6DD, indicative of interaction, are highlighted in blue.