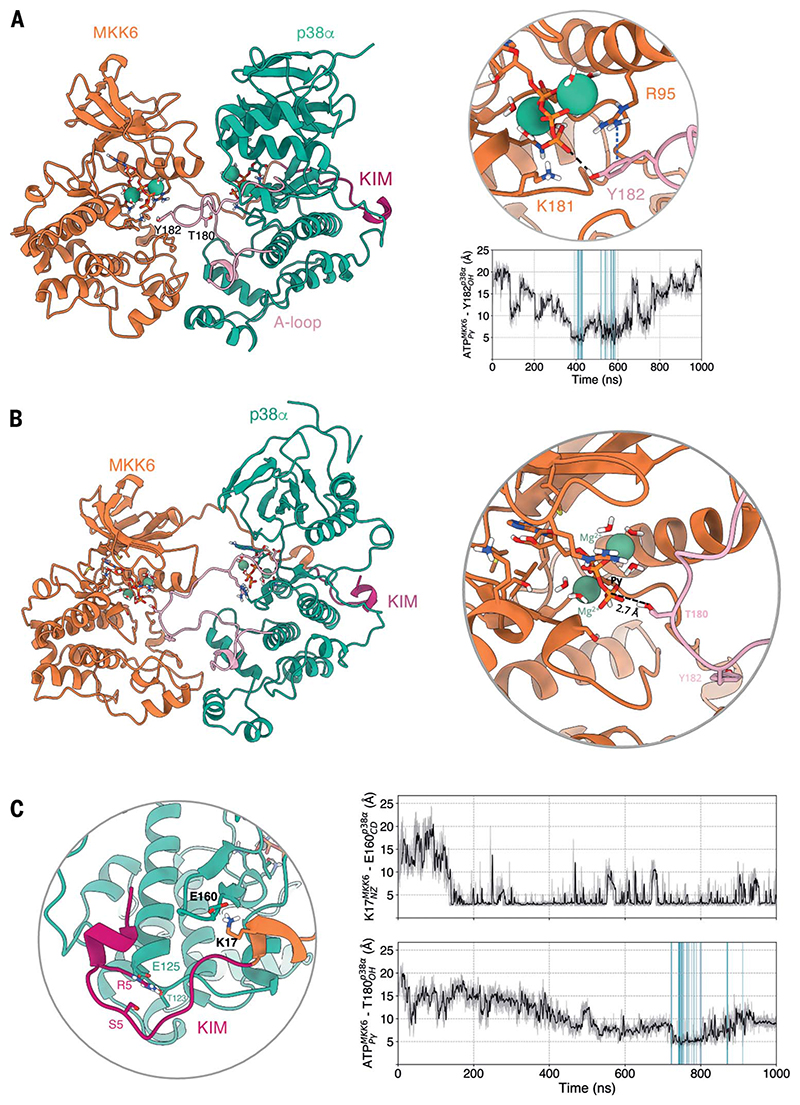
Fig. 3. MD simulations show that both p38α Y182 and T180 can approach MKK6 ATP and that a rotated conformation of p38α favors T180 phosphorylation.
(A) Frame extracted from one of the unrestrained MD simulations in which Y182 approaches the γ-phosphate of MKK6 ATP at a catalytically compatible distance (3.8 Å). The p-cation interaction of R95 with Y182 that further stabilizes Y182 close to ATP is shown in a blue dashed line. The frames where p38α Y182 reaches MKK6 ATP at a catalytically compatible distance in this set of simulations are highlighted in the plot of distances over time (blue). (B) Simulation frame in which p38α has rotated around its axis with respect to the cryo-EM structure. (C) Detailed view around the KIM. The frames where T180 reaches MKK6 ATP at a catalytically compatible distance in this set of simulations are highlighted in the plot of distances over time (blue).