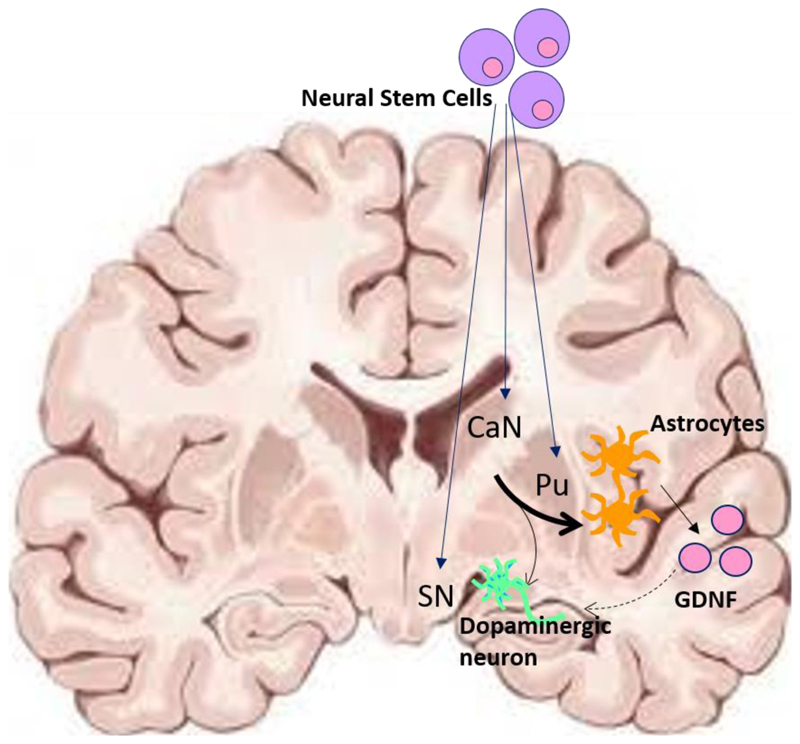
Fig. 1. Putative mechanism of action of parthenogenetic neural stem cells for the treatment of PD.
Neural stem cells (NSCs) are implanted at multiple sites — the caudate nucleus (CaN), the putamen (Pu) and the substantia nigra (SN) — and allowed to terminally differentiate in vivo. NSCs typically differentiate into small populations of dopaminergic neurons and astrocytes, which may supply neurotrophic support in the form of GDNF to the intrinsic and grafted dopaminergic neurons/fibres. The weight of the arrows provides an indication of conversion efficiencies in vivo. The dotted arrow represents neurotrophic support.