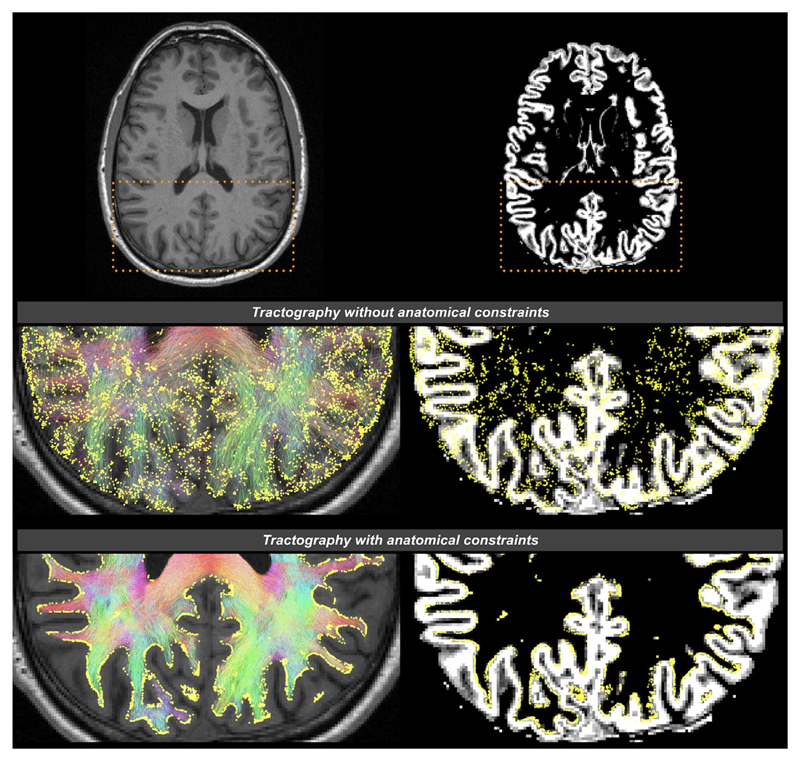
Figure 3.
The effects of applying anatomical constraints on diffusion MRI streamlines tractography, shown on a transverse slice image of a human brain. The background images are a structural T1-weighted image on the left column, and the corresponding gray matter partial volume map following tissue segmentation on the right column. Streamlines are color-coded according to their orientations (red: left–right; green: anterior–posterior; blue: inferior–superior). The yellow spheres are the streamline endpoints. Top row: The dashed boxes indicate the zoomed brain areas shown in the middle and bottom rows. Middle row: Streamlines generated without anatomical priors; streamline endpoints distribute throughout the brain. Bottom row: Streamlines generated with anatomical priors; streamline endpoints only occur at the interface between GM and WM (demonstrated using Refs. 35, 42). It has been revealed that the considerable improvements in such streamline terminations provided by the use of anatomical constraints have significant influences on structural connectivity patterns and the outcomes of connectomic metrics.43,44