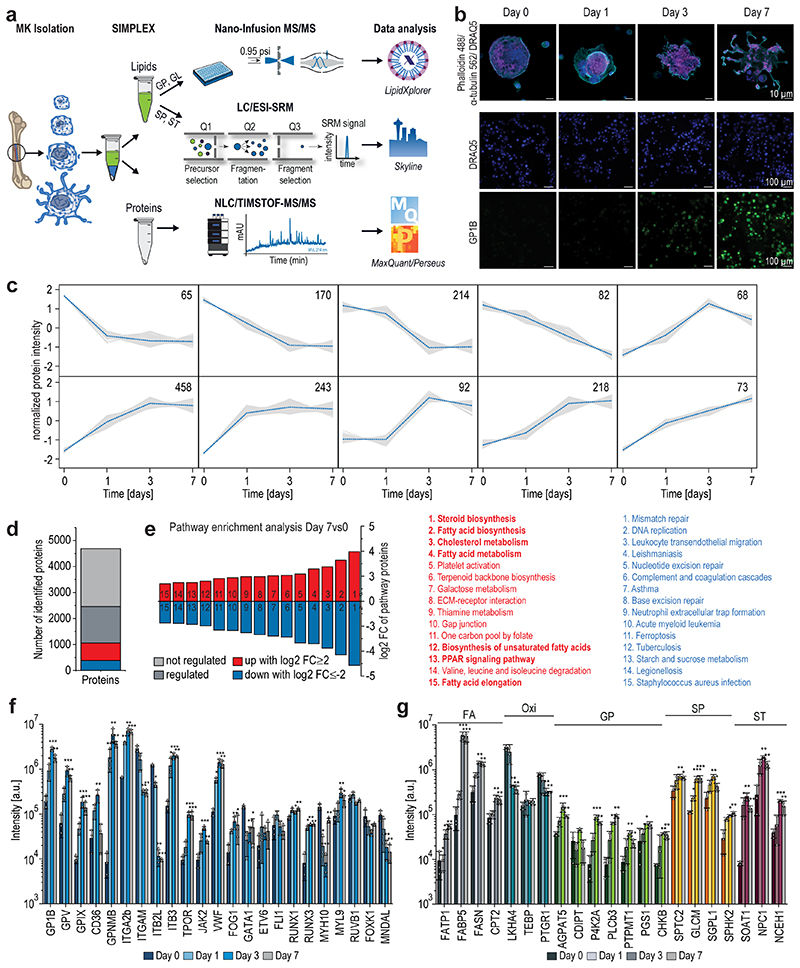
Fig. 1. Global proteomics analysis highlights key changes of proteins steering MK maturation.
a, Multiomics workflow for the quantitative assessment of the lipidome and proteome of maturating megakaryocytes.
b,Representative immunofluorescence staining of GP1B (platelet glycoprotein Ib beta chain, green) expressed in the late stage of MK maturation and platelets (n=6). Nuclei were stained with DRAQ5 dye (blue). Scale bar equals 10 (upper panel) and 100 (lower panel) μm.
c, Fuzzy c-means clustering of regulated proteins from day 0 to day 7. Number of proteins and their median are denoted in individual plots and only a selection of clusters is shown. Note over 2229 proteins are not regulated and therefore not considered. The assignment of proteins to clusters can be found in the Source Data. Threshold = 85.
d, Diagram showing non-regulated (light grey) and significantly regulated proteins comparing day 7vs0, with the latter being divided into three sections: up (red)- or down (blue)-regulated proteins with a log2 FC ≥2 or ≤-2, respectively, and other regulated proteins (dark grey) with log2 FC between -2 and +2.
e, Pathway enrichment analysis of significantly regulated proteins with log2 FC ≥2 or ≤-2 showing the top 15 enriched pathways of only up (red)- or down (blue)-regulated proteins. Pathways were sorted by their fold enrichment independent of the number of proteins involved. Pathway enrichment analysis was performed using the open-source DAVID bioinformatics tool.
f,g, Bar graphs of various MK differentiation markers (f) as well as lipid-related enzymes (g) displayed with their associated lipid category. Proteomics data were combined from 3 independent experiments with 4 pooled mice per biological replicate. Means are displayed with the standard deviation represented as error bars. A two-sided t-test was used for statistical analysis. Benjamini Hochberg correction was applied to p-values using an FDR cut-off < 0.05 (*P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001). FA, free fatty acid; Oxi, oxylipin; GP, glycerophospholipid; SP, sphingolipid; ST, sterol.