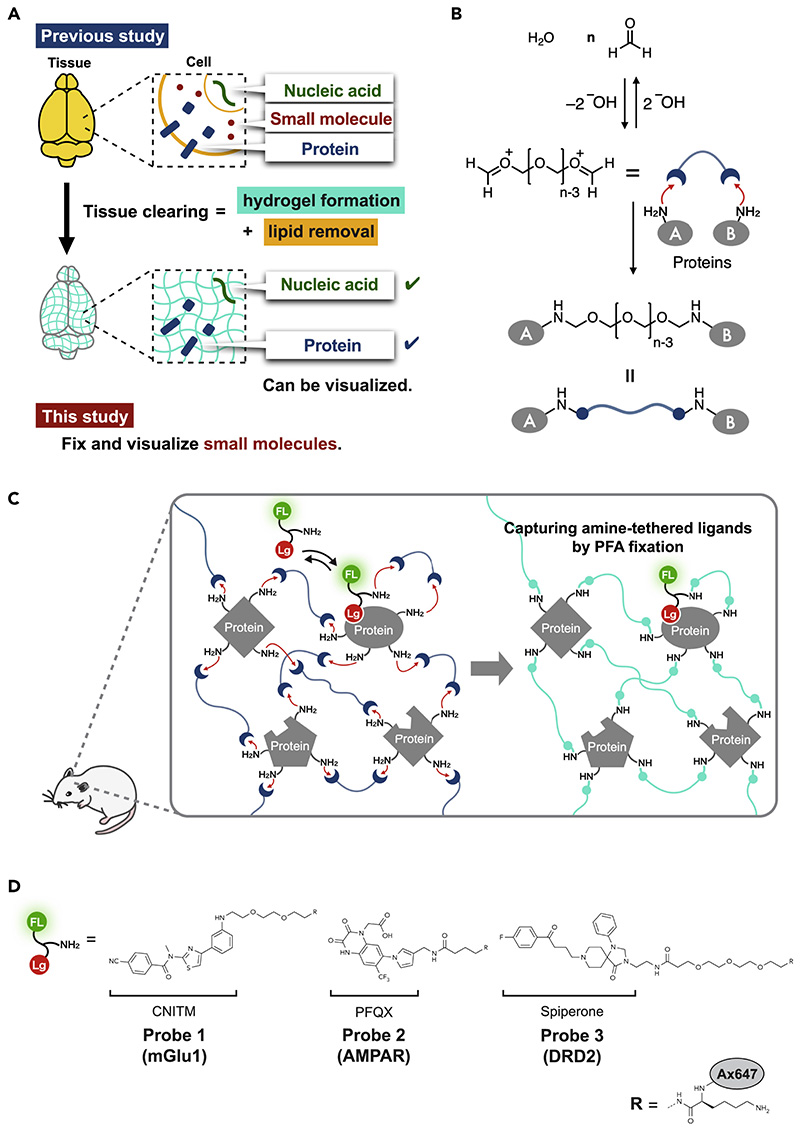
Figure 1. Fixation-driven chemical cross-linking of exogenous ligands (FixEL) in the mouse brain.
(A) The contribution of hydrogel-tissue chemistry (HTC) and a remaining challenge.
(B) Schematic illustration of protein cross-linking by PFA.
(C) Schematic illustration of the FixEL strategy. FL and Lg refer to fluorophore and ligand, respectively.
(D) FixEL probes used in this study. Probe 1 (mGlu1) has a CNITM moiety, which is a ligand for mGlu1, and an amino group. Probe 2 (AMPAR) has a PFQX moiety, which is a ligand for AMPAR, and an amino group. Probe 3 (DRD2) has a spiperone moiety, which is a ligand for DRD2, and an amino group.