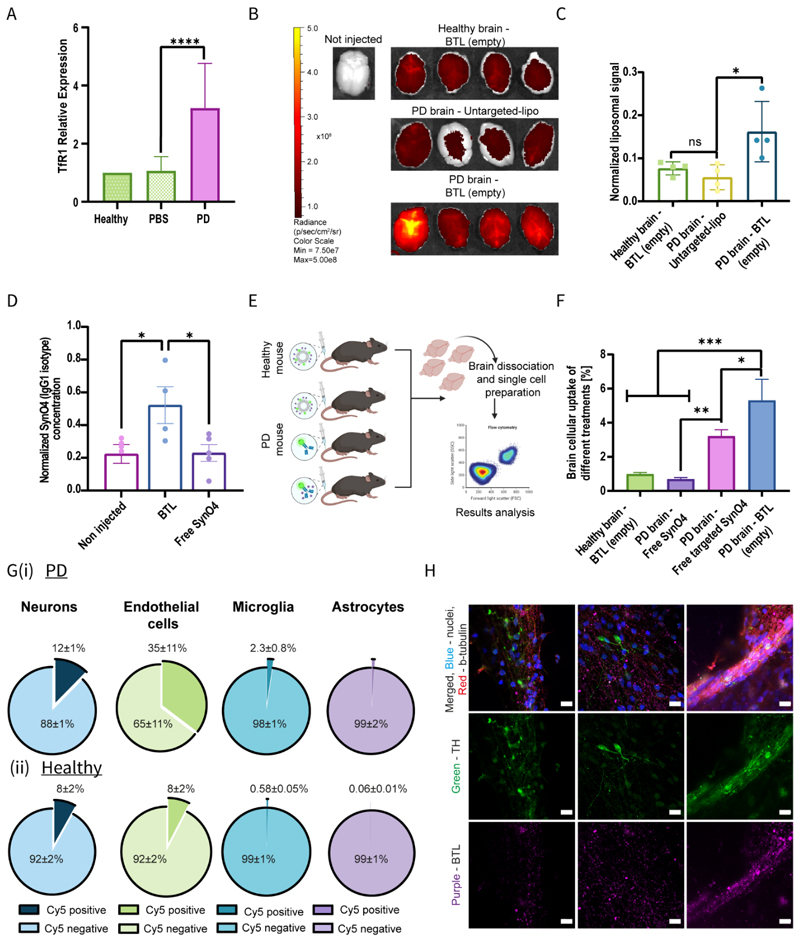
BTL cross the BBB and significantly accumulate in PD mice brains.
(A). RT-qPCR analysis of TfR1 expression in the PD brain; TfR1 expression levels were normalized to those of the healthy group and were obtained according to the 2^(-∆∆Ct) method. (B-C). Nanoparticle biodistribution in the brains of PD-induced and healthy mice 12 h post-administration of Cy5-labeled BTL (empty) or Cy5-labeled untargeted liposomes, analyzed using an in-vivo imaging system (IVIS) (B) and quantified by IVIS software analysis (C). (D). Levels of the IgG1 isotype (SynO4 isotype) in PD brains following liposome delivery or antibody delivery, as determined using ELISA. (E). Schematic diagram illustrating the flow cytometry setup experiment. (F). The levels of BTL (empty), transferrin-SynO4 mAb, and free SynO4 mAb in PD brain cells and those of BTL in healthy brains were determined using flow cytometry. (G). Quantification of BTL cellular uptake in neurons, endothelial cells, microglia, and astrocytes in (i) PD brains and (ii) healthy brains. (H). Confocal imaging of BTL cellular uptake in human PD dopaminergic neurons. The liposomes were labeled with Cy5 (purple), and cells were stained with tyrosine hydroxylase (TH, green), b-tubulin (red), and nuclei (blue) (scale bar: 10 um). Results of A, C, and E (5 independent repetitions) and D and F (4 independent repetitions) are presented as mean±standard deviation (SD). One-way ANOVA with an adjusted p-value in multiple comparison tests was used for statistical analysis in A, C, D, and F; *p≤0.1061, **p≤0.0065, ***p≤0.0002, ****p<0.0001. BBB, blood-brain barrier; BTL, brain-targeted liposomes; PD, Parkinson’s disease. RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative PCR; TfR1, transferrin receptor.