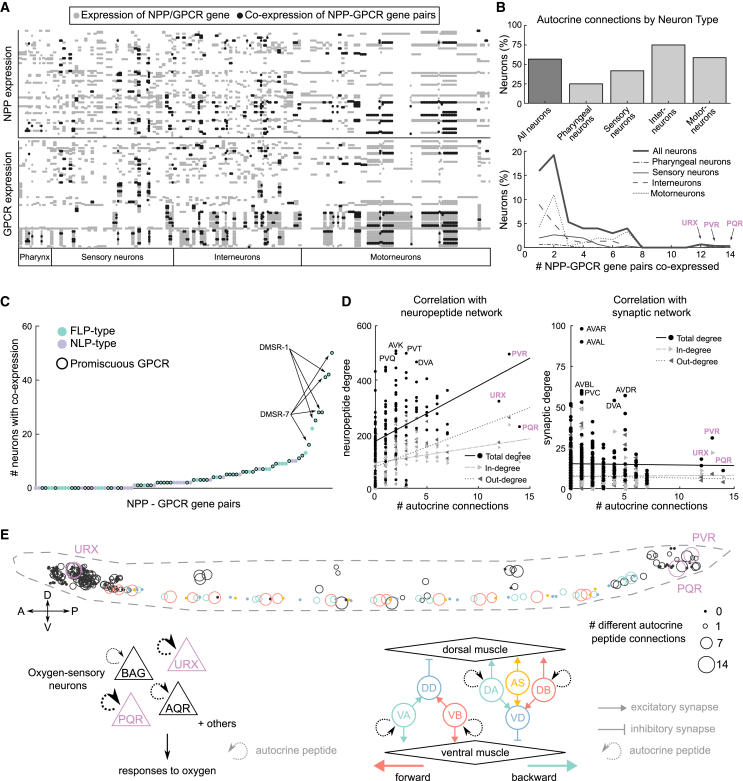
Figure 8.
Co-expression between GPCRs and their ligands potentiates autocrine and paracrine signaling
(A) Neuronal expression matrix for NPP and GPCR genes of the 92 NPP-GPCR pairs. Gray dots represent expression of only the NPP (upper panel) or GPCR (lower panel), black dots indicate co-expression.
(B) Percentage of each neuron type showing peptide autocrine connections (upper panel). The number of different NPP-GPCR pairs co-expressed in each neuron type is shown in the bottom panel.
(C) Scatter plot showing the number of neurons with co-expression for each of the 92 NPP-GPCRs.
(D) Correlation between number of autocrine connections and neuropeptide (left) or synaptic (right) degree for each neuron. Point shapes indicate degree (round), in-degree (incoming arrow), and out-degree (outgoing arrow).
(E) Locations of autocrine connections in the worm. Cell body size indicates the number of autocrine NPP-GPCR pairs expressed in that neuron. Colored neurons (including those of the oxygen-sensing and locomotor circuits, diagrammed below) exhibit the largest number of autocrine connections. Arrow size indicates number of NPP-GPCR pairs.