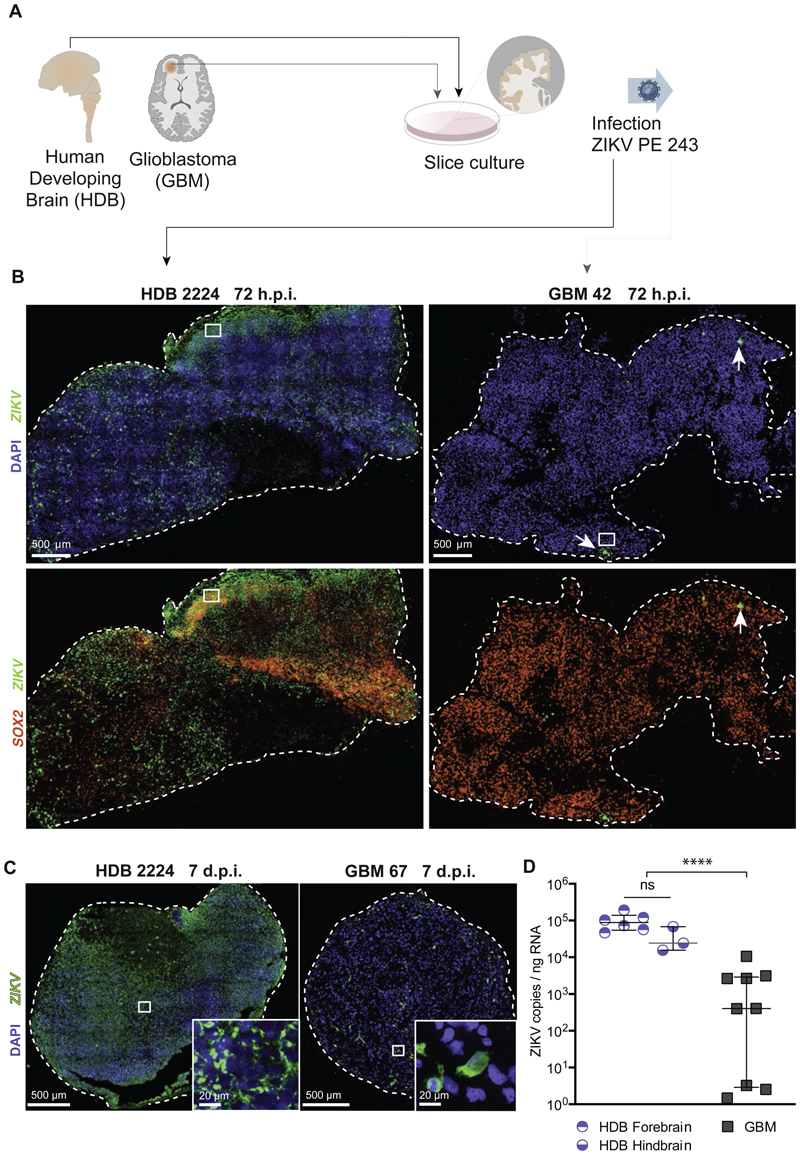
Figure 1. Human developing brain organotypic slices are vulnerable to ZIKV whereas GBM slices are refractory.
(A) Primary HDB and GBM samples were processed for slice culture, then infected with ZIKV PE243.
(B) RNAscope smFISH of representative ZIKV-infected HDB and GBM slice cultures with ZIKV 1x10^7 PFU, 72 hours post infection (h.p.i.), using SOX2 (red) and ZIKV (green) probes. White arrow denote ZIKV infection.
(C) smFISH of ZIKV-infected HDB and GBM slice cultures with ZIKV 1x10^7 PFU, 7 days post infection (d.p.i.), using ZIKV probe (green).
(D) RT-qPCR of ZIKV in HDB and GBM slice cultures, infected with ZIKV 1x10^7 PFU, 7 d.p.i., (Median and interquartile range indicated. **** Mann Whitney U t-test p <0.0001). Data points represent replicate slices from HDB n=2 specimens, both with hb and fb regions, and GBM n=3 patients.