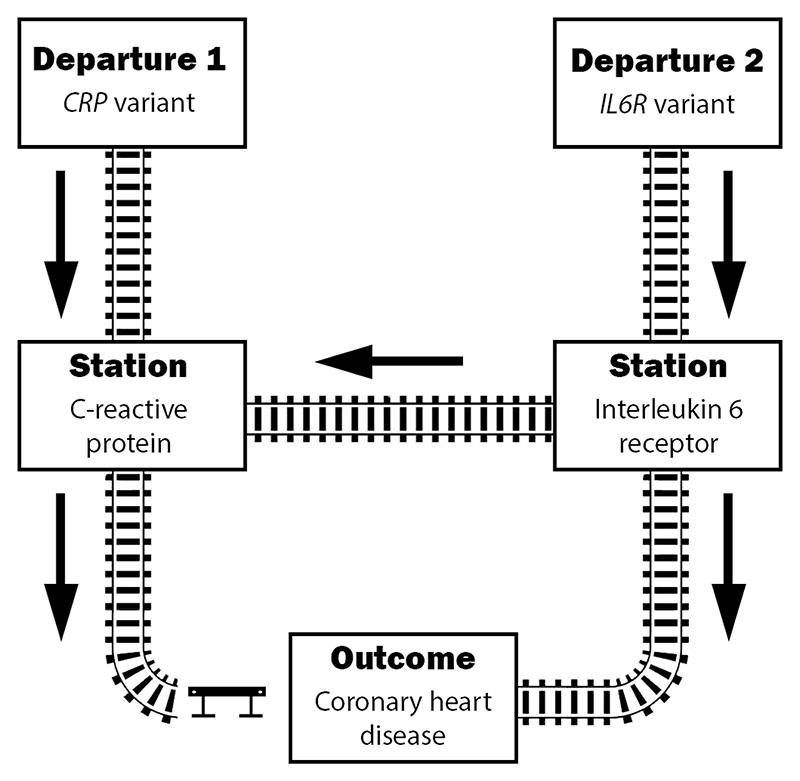
Figure 2. Railway network illustrating pathways linking inflammatory traits to coronary heart disease.
Trains leaving from departure station 1 (variant in CRP gene region) pass first through C reactive protein, whereas trains leaving from departure station 2 (variant in IL6R gene region) pass first through interleukin-6 receptor and then branch out either to C reactive protein or directly to the outcome. As variants in the CRP gene region do not associate with the outcome that railway line is blocked by the buffer stop/stopblock. Variants in the IL6R gene region do associate with the outcome, implying that there is a functioning route from departure station 2 to the outcome. However, due to the buffer stop on the route from C reactive protein to the outcome, the effect of interleukin-6 receptor on the outcome must be direct and not via C reactive protein, and hence interleukin-6 receptor is a causal risk factor for coronary heart disease, but C reactive protein is not.