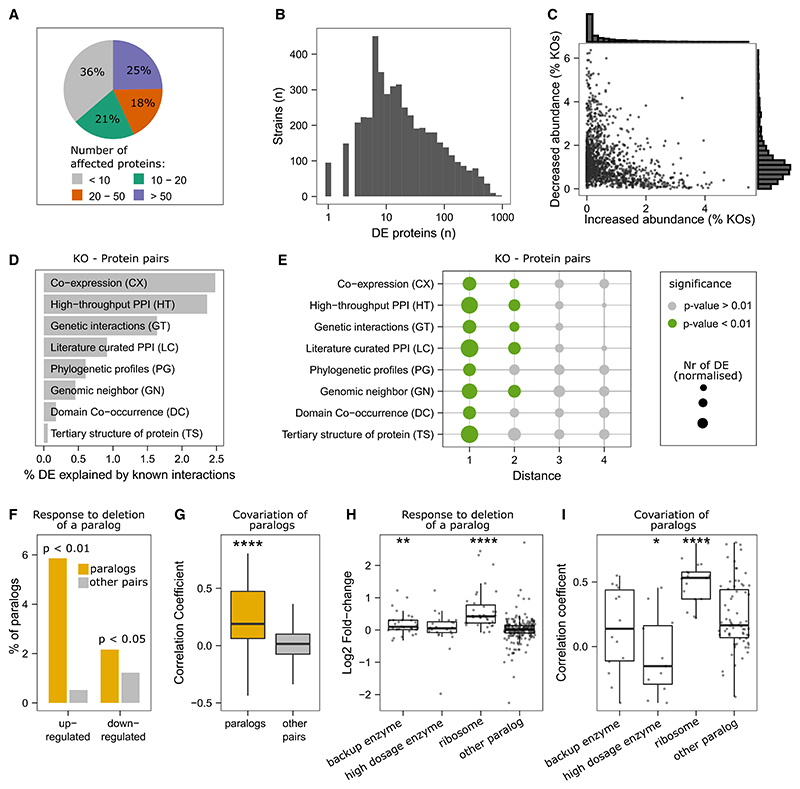
Figure 2. The proteomic response to systematic gene deletion.
(A) Fraction of gene deletion strains (n = 4,699) in which proteins are differentially expressed (STAR Methods).
(B) Distribution of proteomic responses, given as the number of differentially expressed proteins (DE; Benjamini-Hochberg (BH)-adjusted p value < 0.01).
(C) Increased and decreased abundance of each protein across the 4,699 KO strains are given as dots and as histograms.
(D) Differentially expressed proteins upon gene deletions were compared with physical, genetic, or functional interactions, collected as part of the YeastNet resource (v3).34
(E) Differential abundance of proteins is related to their distance to the deleted gene in the indicated network. Differentially abundant proteins of distance i were normalized to the total number of proteins of distance i within the respective network. A significant enrichment (hypergeometric test, p value < 0.01) is indicated by color.
(F) Percentage of paralogs from whole-genome duplications (ohnologs)35 that have increased or decreased abundance (BH-adjusted p value < 0.01) after the deletion of one of the paralog partners (yellow). The number of increased or decreased proteins across all KOs is shown as a gray bar for reference.
(G) Spearman correlation coefficients are shown for ohnologs35 (n = 107 pairs) and for all other protein pairs (n = 1,710,215). The median correlation coefficients are 0.19 and 0.01 for paralogs and other pairs, respectively (Wilcoxon signed-rank test; ****p value ≤ 0.0001). (H) paralogs were classified as compensatory enzymes (backup); enzymes duplicated to increase gene dosage36; or protein components of the ribosome (according to the GO term “structural constituent of ribosome37”), and compared with measured paralogs not categorized according to these groups (“other paralogs”) (**p value ≤ 0.01; ****p value ≤ 0.0001, Student’s t test).
(I) Correlation coefficients are based on Spearman rank coefficients and compared to measured paralogs not categorized (“other paralogs”) (*p value ≤ 0.05; ****p value ≤ 0.0001; Student’s t test).
See also Figure S2.