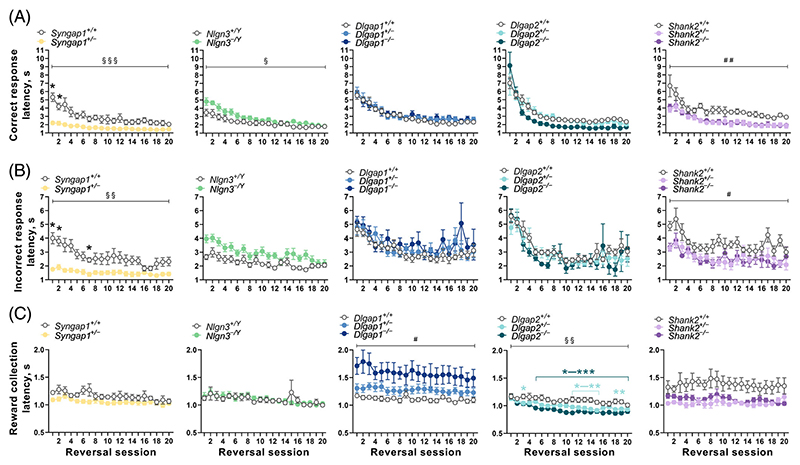
Figure 5.
Reaction times during reversal learning. Session-level analysis across reversal learning compound sessions. Latencies to make (A) correct or (B) incorrect responses and (C) to collect rewards following a correct response are illustrated. Significant genotype × compound session interaction (indicated as §p < 0.05; §§p < 0.01; §§§p < 0.001) was followed by post hoc Holm-Šidák multiple comparisons tests to reveal differences between mutant mice and WT littermates at individual sessions with significant effects being indicated as follows: *p < 0.05;**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Significant main effects of genotype are indicated as follows: #p < 0.05; ##p < 0.05. All original p values associated with the effects of genotype, session and genotype × compound session interaction were adjusted for multiple comparisons using the Holm–Šídák correction. +/− heterozygous, −/Y hemizygous, −/− homozygous, +/+ WT