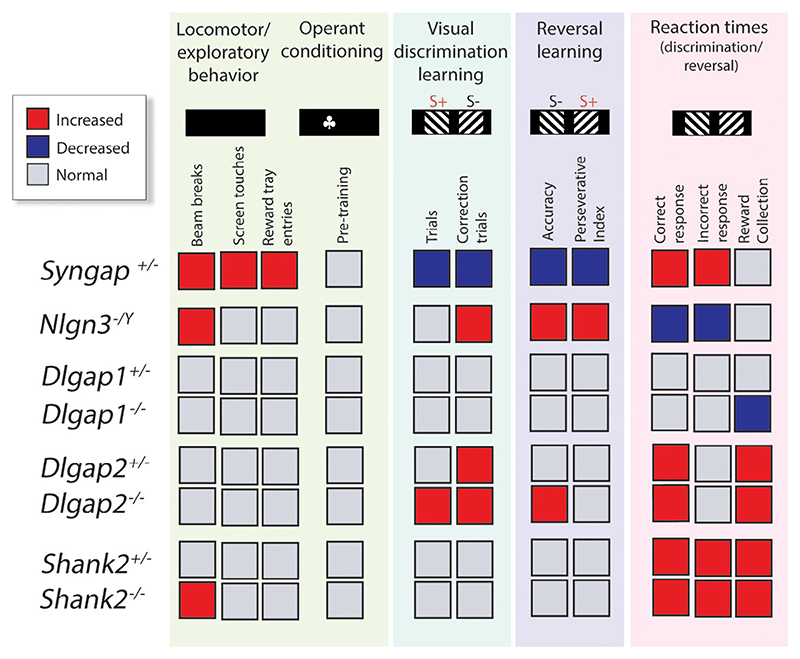
Figure 6.
Summary of cognitive phenotypes. Mutations in Syngap1, Nlgn3, Dlgap1, Dlgap2 and Shank2 genes lead to specific changes in different measures of learning and reaction times that underlie cognitive processing. Female Syngap1, Shank2, Dlgap1 and Dlgap2 mutant mice were behaviourally assessed at the Babraham Institute, Cambridge UK, and male Nlgn3 mutant mice were behaviourally tested at the Florey Institute, Melbourne Australia. Locomotor and exploratory behaviour during habituation to the touchscreen chambers (Front and back chamber beam breaks; Touchscreen touches; Head-entries into reward magazine); Operant conditioning (acquisition of touchscreen pre-training stages); Visual discrimination learning (Trials, first presentation; Correction trials); Reversal learning (Accuracy, % correct response; Perseverative Index); Reaction times (Correct response latency; Incorrect response latency; Reward collection latency) during visual discrimination and reversal learning. +/− heterozygous, −/Y hemizygous, −/− homozygous