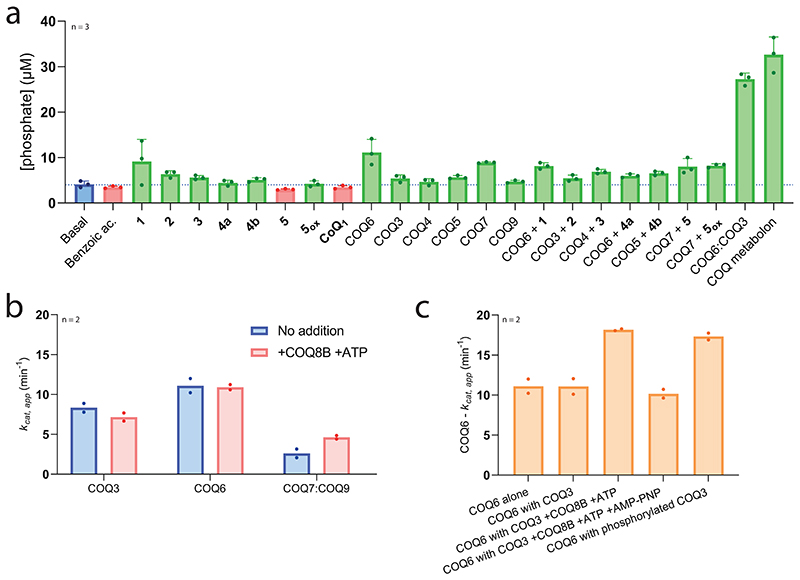
Extended Data Fig. 8 |. Dissecting the role of COQ8B in CoQ biosynthesis.
a. COQ8B ATPase activity is stimulated by COQ proteins and intermediates. Micromolar concentration of inorganic phosphate released via ATP hydrolysis by COQ8B in a series of conditions. Concentrations were determined after 10 minutes following a calibration line of analytical standard of phosphate reacted with the Malachite green dye (Supplementary Fig. 12). The phosphate concentration produced by COQ8B in the absence of any COQ substrate or protein (ca. 4 μM) is shown as a blue bar and dashed line. Individual data points corresponding to n = 3 independent measurements are shown. The bars of the histogram show the mean value of independent replicates. The error bars correspond to the standard deviations in n = 3 independent measurements for each datum. b. COQ8B promotes activity for paired COQ proteins. COQ8B (1 μM) and ATP (10 μM) does not boost COQ3 and COQ6 activity, and marginally for COQ7:COQ9 as measured by substrate consumption. c. COQ6 activity is boosted by COQ8B and ATP only if in the presence of COQ3. As a further control, the role of COQ8B was evaluated by competition of ATP with AMP-PNP (Adenosine 5’-(β,γ-imido)triphosphate; 100 μM), a non-hydrolysable ATP analogue. COQ3, previously phosphorylated by pre-incubation with COQ8B and ATP, provided a comparable increase in COQ6 activity. Phosphorylated COQ3 was generated by incubation with COQ8B, and ATP followed by size-exclusion chromatography purification. Individual data points corresponding to n = 2 independent measurements are shown in panels b-c. The bars of the histogram show the mean value of independent replicates.