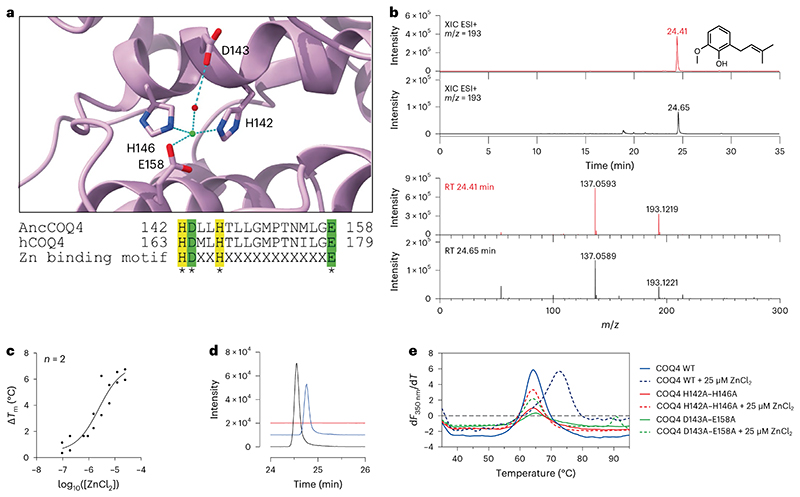
Fig. 3 |. C1 decarboxylation is performed by COQ4 in a Zn2+-dependent manner.
a, Close-up of the putative Zn2+-binding site in the predicted COQ4 AlphaFold model, and alignment of human and ancestral COQ4 with the Zn2+-binding motif highlighted. Residues involved are shown as sticks, and Zn2+ ion is shown in green and water molecules in red. b, UHPLC/HRMS analysis of the overnight COQ4 conversion of 3 into 4a. The XICs and ESI+ full-scan mass spectra of 4a recorded after the injection of 500 ppm analytical standard and of the reaction mixture are shown in red and black, respectively. The theoretical mass of the [M + H]+ molecular ion of 4a is 193.1223 Da. It was detected with an error of −2.07 and −1.04 ppm in the analyses of the standard and sample, respectively. RT, retention time. c, Dose−response plot of the thermostabilizing effect provided by ZnCl2 on COQ4. d, Waterfall plot showing a qualitative analysis of UHPLC peak of 4a produced by COQ4 in the presence (black) or absence (blue−time offset 0.2 min) of 25 μM ZnCl2 and in presence of 1mM EDTA (red−time offset 0.4 min). e, First derivative plot of nano-differential scanning fluorimetry analyses on COQ4 wild type (WT) and double mutants. The Tm corresponds to the peak of the first derivative. Individual data points corresponding to n = 2 independent measurements are shown in c.