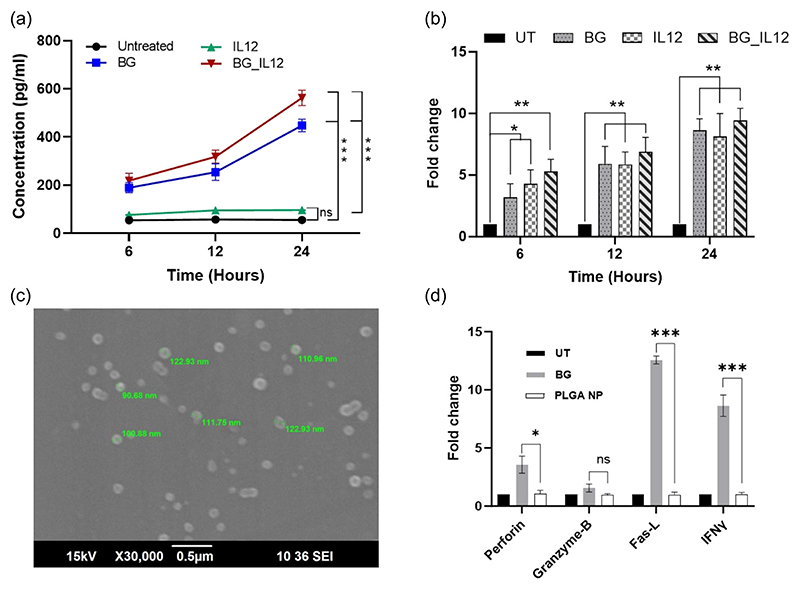
Figure 5. Protein quantification and gene expression analyses.
(a) Quantification of IFN-γ protein content in the supernatant of BG, IL12, and BG_IL12-treated NK-92 cells at specific time points using a sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). (b) Relative fold change of IFN-γ gene expression estimated using qPCR via the 2–ΔΔCt method for BG, IL12, and BG_IL12-treated NK-92 cells compared to the untreated control, with GAPDH as reference. (c) Scanning electron micrograph of PLGA nanoparticles prepared via nanoprecipitation. (d) Relative fold change of gene expression in NK-92 cells treated with BGs and PLGA nanoparticles performed using the 2–ΔΔCt method via qPCR for perforin, granzyme-B, Fas-L and IFNγ, compared to the untreated control, with GAPDH as reference. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, ***p < 0.001 and ns: not significant. BG, bacterial ghost; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; IFN, interferon; NK, natural killer.