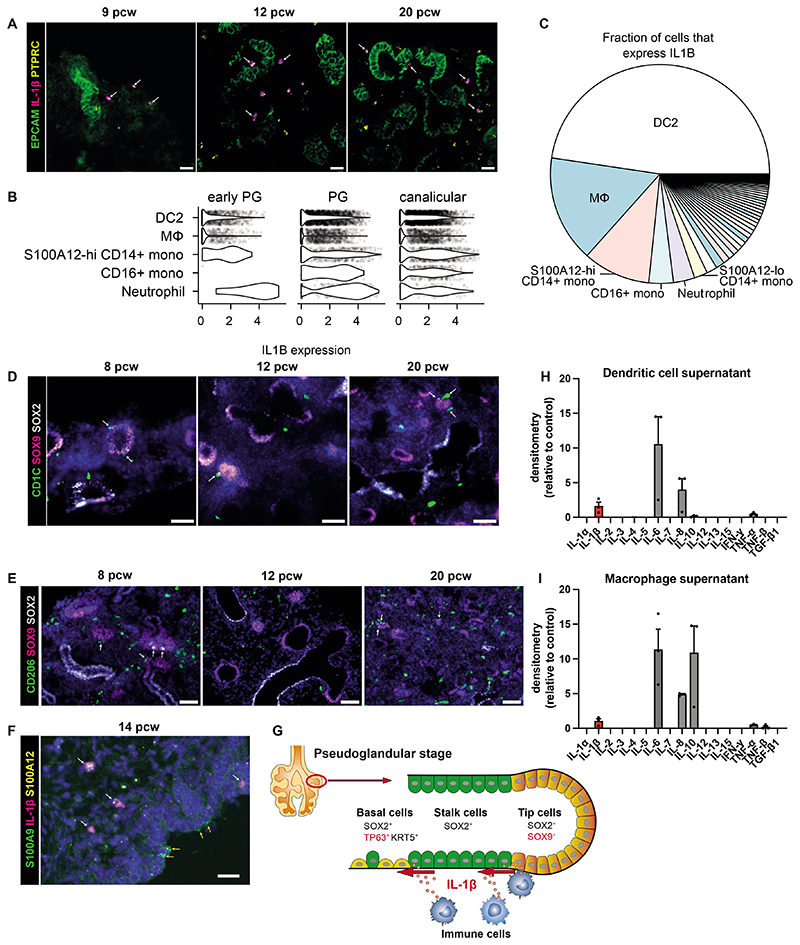
Figure 7. Fetal lung myeloid cells secrete IL-1β.
(A) RNAscope images of fetal lungs, showing expression of PTPRC and IL1B, with EpCAM IHC (white arrows: PTPRC+IL1B+ cells; scale bar=20μM). (B) Violin plot showing IL1B gene expression in each of the top 5 highest expressing cell types, based on our single-cell dataset (Fig S8 shows all cell types). (C) Pie chart showing the total contribution of each cell type to all expressed IL1B mRNA. IHC images show the distribution of CD1C+ DC2 cells (D) or CD206+ macrophages (E) surrounding SOX9+ epithelial tips during lung development (white arrows: immune cells adjacent to SOX9+ cells; blue: DAPI+ nuclei; scale bar=50μM). (F) RNAscope image showing the distribution of S100A9+S100A12+ neutrophils/monocytes relative to the epithelium (determined morphologically), including those that coexpress IL1B (white arrows) and those that do not (yellow arrows) (blue: DAPI+ nuclei; scale bar=20μM). (G) Model: IL-1β causes exit from a self-renewing state and airway differentiation during fetal lung development. Isolated DC or macrophages (via FACS of 19-21 pcw lungs, Fig S1D) were cultured for 7 days to investigate cytokine production. The pooled supernatant, from days 3, 5 and 7 of culture, was analyzed using the Human Cytokine Antibody Array (abcam; H and I respectively, n=3 biological replicates). See Fig S10.