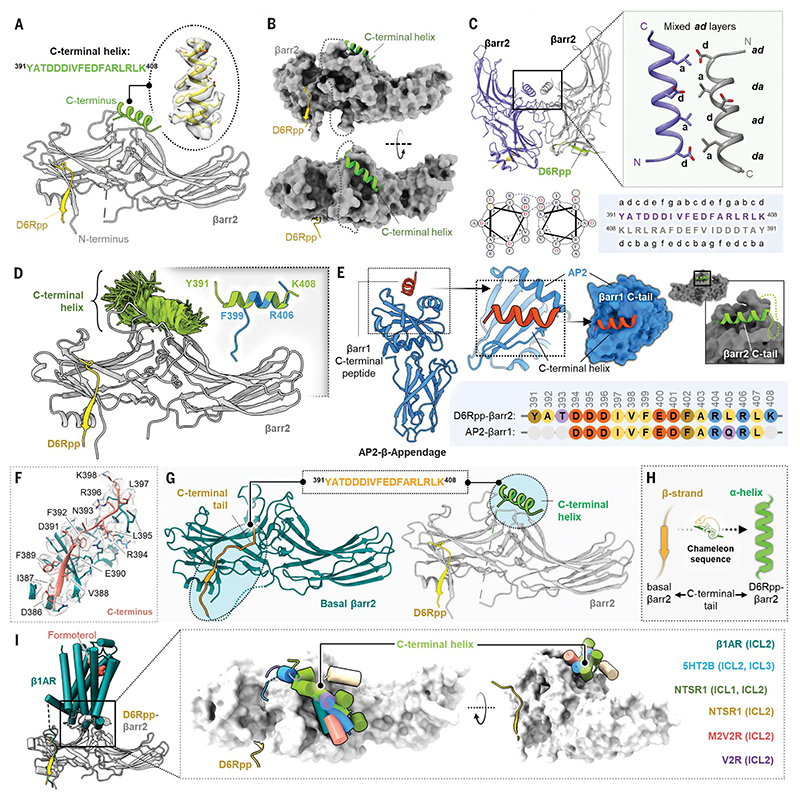
Fig. 4. Discovery of a C-terminal helix in D6R-activated βarr2.
(A) Cartoon representation of βarr2 bound to D6R phosphopeptide. βarr2 and D6Rpp are presented in gray and yellow, respectively, and the sequence of the C-terminal helix is shown in the inset. (B) D6Rpp-βarr2 structure displayed in surface representation in two different views to highlight the pose of the helix. The C-terminal helix (green) and D6Rpp (yellow) are shown as ribbon diagrams. (C) Dimeric organization of D6Rpp-βarr2 structure shown in ribbon representation (top left). Formation of antiparallel coiled-coil by the C-terminal helix of βarr2 at the dimeric interface (top right) shown as cartoon representation. The antiparallel coiled-coil exhibits mixed ad layers. Helical wheel representation of the antiparallel coiled-coil shows Asp at position d of one helix, which forms a salt bridge with Arg at position g in the other helix (bottom left). Heptad helical representation of the antiparallel coiled-coil residues in the βarr2 sequence (bottom right). (D) MD simulations confirm stability of the distal C-terminal helix/βarr2 interface. Structural snapshots (one snapshot every 10 ns, 7 × 250 ns of simulation time) presented here are of the position of the C-tail during simulation. For each residue, frames where it assembles an α-helical conformation are colored green. Fragments of the C-terminal helix can spontaneously assemble an a-helical conformation (right corner, blue cartoon) in three out of four independent MD simulations (each 2 μs) which is overlayed with the crystallized C-tail for comparison (green cartoon). For each residue, frames where it assembles a helical conformation are colored green. Comparison of a spontaneously assembled helical conformation of the βarr2 C-tail (blue) with that present in the structure (gray). (E) Structure of AP2 b-appendage protein in complex with βarr1 C-terminal peptide (PDB ID 2IV8) is shown as cartoon representation (left). The βarr1 C-terminal peptide can be seen to adopt similar helical conformation as the C-terminal helix in the D6Rpp-bound βarr2 structure (right). The sequence alignment of the C-terminal stretches of βarr1 and βarr2 are shown in the inset. (F) Cryo-EM density map of the isolated C terminus of βarr2 and surrounding residues within 4Å. (G) The peptide stretch sequence (top) of the C-tail in basal βarr2 transforms into a helical conformation in the D6Rpp-bound state (highlighted in cyan circles). (H) The C-tail of βarr2 exhibits a chameleon-like property, adopting a helical conformation in the active state from a β strand in the basal state. (I) Ribbon representation of the β1AR-βarr1 structure superimposed with D6Rpp-βarr2 on βarrs (left) shows positioning of the C-terminal helix on the central crest of βarrs. Upon structural superimposition with all reported GPCR-βarr1 structures, ICL1/2/3 of various receptors reside on the central crest as a C-terminal helix on D6Rpp-βarr2 (right).