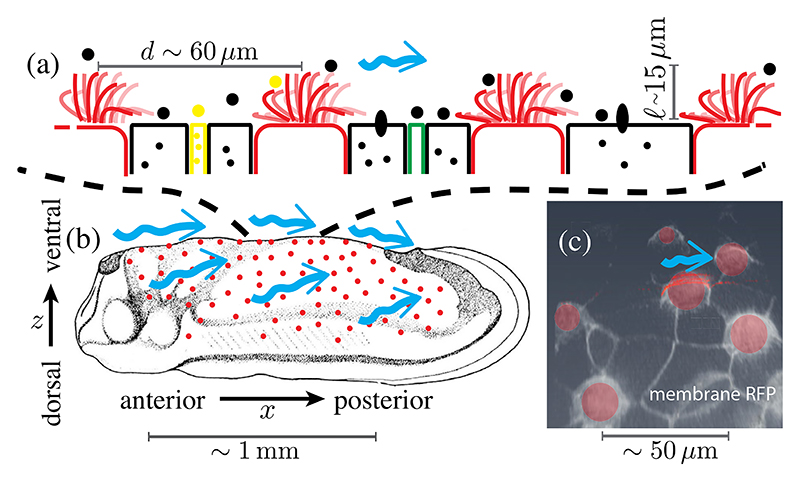
Fig. 1. Ectoderm of embryonic Xenopus laevis at tailbud stages.
(a) Schematic side view of MCCs (red) intermixed with secreting cells. (b) Location of MCCs across the embryo (adapted from Refs. [22,23]) and cilia-driven flow (blue arrows). (c) Con-focal image of cell membranes (stained by membrane-RFP), with MCCs segmented in red, in ventral region of skin.