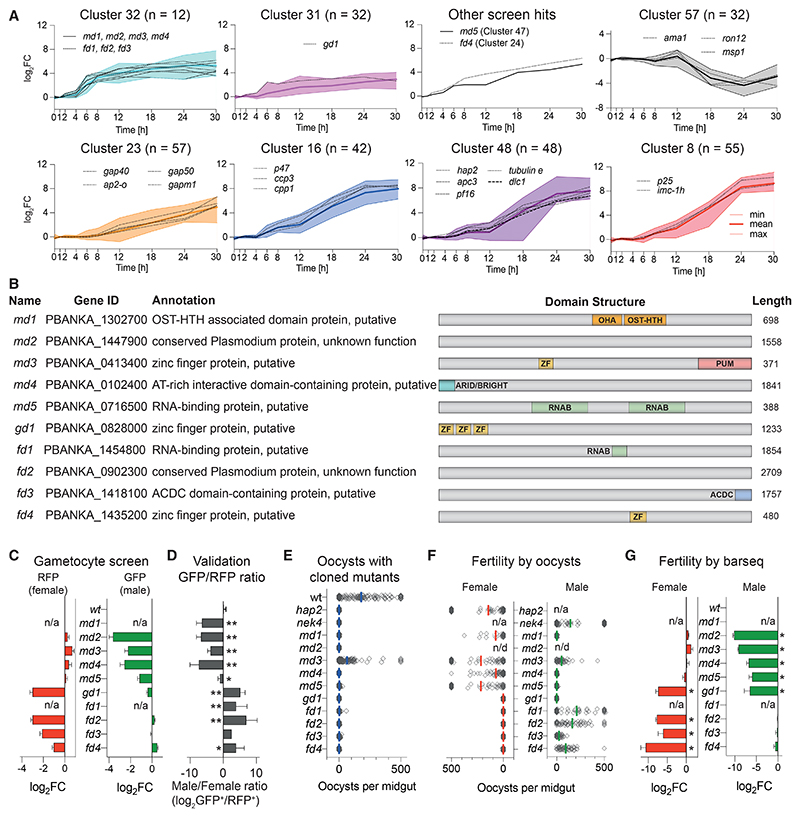
Figure 2. Selection and validation of ten P. berghei genes with sex-specific roles in gametocytogenesis.
(A) Selected gene expression clusters from a bulk RNA-seq time course of induced sexual development. Ring-stage parasites were reprogramed at t = 0 h by inducing ap2-g.6 Relative transcript abundances are given as log2-fold change relative to uninduced, asexually developing parasites. Shown are selected clusters (number of genes) with screen hits designated md, fd, or gd. Selected well-characterized marker genes of male, female, and asexual development are also shown.
(B) Schematic illustration of genes with validated roles in sexual development. OST-HTH, oskar-TDRD5/TDRD7 winged helix-turn-helix domain; OHA, OST-HTH associated domain; ARID/BRIGHT, AT-rich interaction domain; ZN, C3H1 zinc finger; PUM, Pumilio RNA-binding repeat profile; RNAB, RNA-binding domain; ACDC, apetala 2 domain-coincident C-terminal domain; PH-like, PH domain like.
(C) Fold-change (FC) in reporter-positive cells in the bar-seq screen. Error bars show standard deviations.
(D) Sex ratio in individual mutants determined by flow cytometry. Error bars show standard deviations from 2 to 4 biological replicates with cloned mutants, except for fd3, where the uncloned population is shown. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01 in unpaired t test.
(E) Transmission efficiency of mutant clones in vivo determined by counting oocysts on midguts 10 days after an infectious blood meal.
(F) Male and female fertility as determined by the ability of mutant clones to give rise to oocysts in mosquitoes when crossed to nek4 and hap2 mutants, which provide fertile male or female gametes, respectively. Oocysts counts show combined data from 25 to 80 dissected mosquitoes from 2 to 3 independent experiments. n/d, not done; n/a, not applicable.
(G) Fold-change (FC) in female and male fertility determined by bar-seq of 10-day infected midguts following mutagenesis of female-only or male-only lines, respectively. Error bars show standard deviations from four biological replicates. * p < 0.001 in unpaired t test.