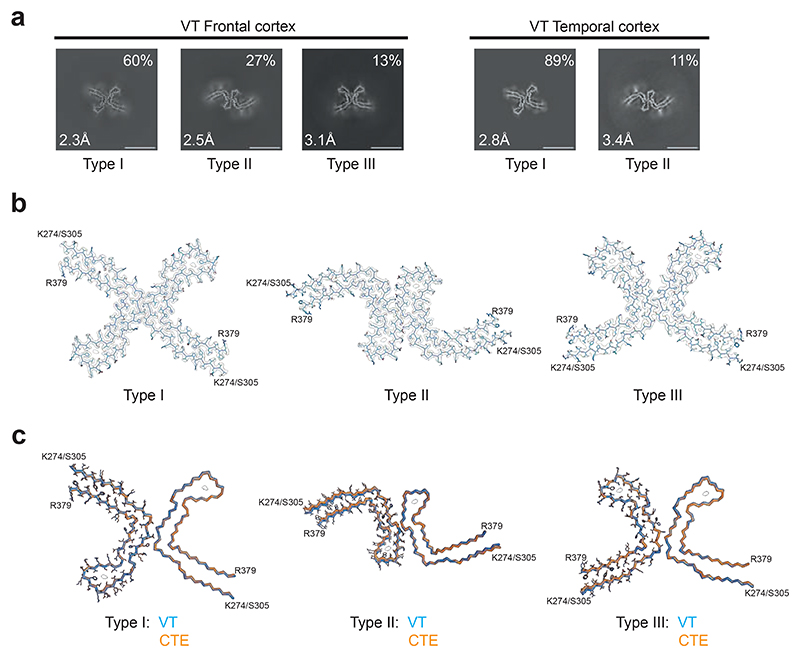
Figure 7. Cryo-EM cross-sections and structures of tau filaments from vacuolar tauopathy.
a, Cross-sections through the cryo-EM reconstructions, perpendicular to the helical axis and with a projected thickness of approximately one rung, are shown for frontal and temporal cortex. Three filament types were present (Type III was only found in the frontal cortex). They are made of two identical protofilaments that are arranged in different ways.
Resolutions (in Å) and percentages of filament types are indicated in the bottom left and top right, respectively. Scale bar, 10 nm.
b, Cryo-EM density maps and models of Type I, Type II and Type III tau filaments from the case with vacuolar tauopathy.
c, Type I, Type II and Type III filaments from the case with vacuolar tauopathy (in blue) overlaid with CTE Type I, Type II and Type III filaments from a case with CTE (in orange). The ordered cores of the filaments extend from tau K274/S305-R379.
The root mean square deviation (rmsd) between Cα atoms of Type I and CTE Type I filaments was 0.28 Å; that between Type II and CTE Type II filaments was 0.57 Å and that between Type III and CTE Type III filaments was 0.57 Å.