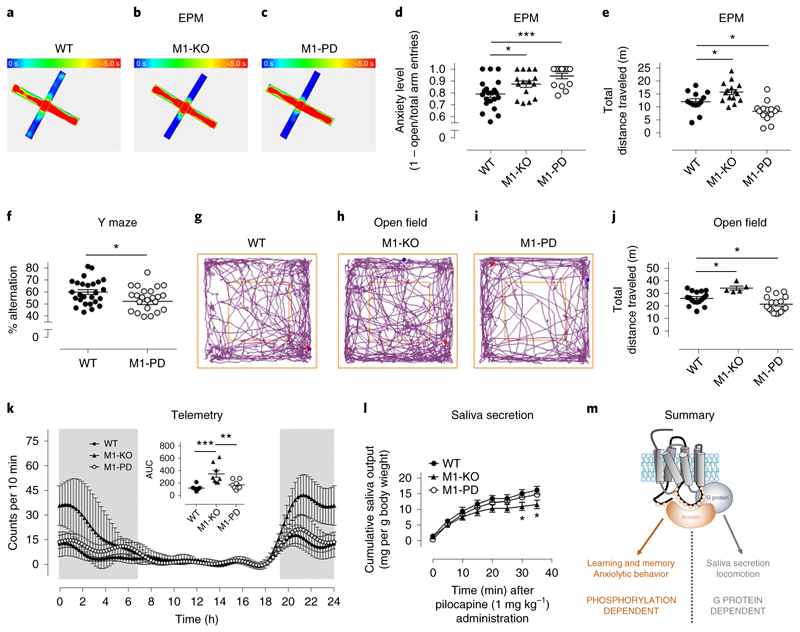
Fig. 4. Mapping of bimodal signaling to M1 mAChR physiological responses.
a–c, Heat maps showing the occupancy of WT (a, n = 13), M1-KO (b, n = 4) or M1-PD (c, n = 14) mice in the open or closed arms of the EPM (blue, 0 s occupancy; red, 5 s occupancy). d, Anxiety level of WT (n = 21), M1-KO (n = 15) or M1-PD (n = 14) mice (calculated as a ratio of open/closed arm entries divided by the total number of entries). e, Total distance traveled in the EPM of WT (n = 13), M1-KO (n = 15) or M1-PD (n = 14) mice. Data in d and e are presented as mean ± s.e.m. and were analyzed using a one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001. f, WT or M1-PD mice were tested for 8 min in a Y maze spontaneous alternation paradigm to assess spatial working memory. Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. and were analyzed using a Student’s t-test. *P < 0.05. g–i, Representative track plots of WT (g), M1-KO (h) and M1-PD (i) mice in the open field test. j, Total distance traveled in a 10 min period by WT, M1-KO and M1-PD mice during an open field test. Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. and were analyzed using a one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. *P < 0.05. k, Basal locomotor activity of WT A, M1-KO and M1-PD mice, assessed using in vivo telemetry recordings. Mean locomotor activity ± s.e.m. of eight mice over a 24 h period is shown, with total locomotor activity during this period calculated by measurement of the area under the curve (AUC). l, Salivary secretion in response to pilocarpine (1 mg kg−1) administration was measured in WT, M1-KO and M1-PD mice. Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. of n = 5–7 mice. Data were analyzed using a one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test compared to WT mice. *P < 0.05. m, An illustration of the M1 mAChR physiological responses lying downstream of G protein-dependent signaling (saliva secretion and locomotion) versus phosphorylation-dependent signaling (anxiolytic behavior and spatial working memory).