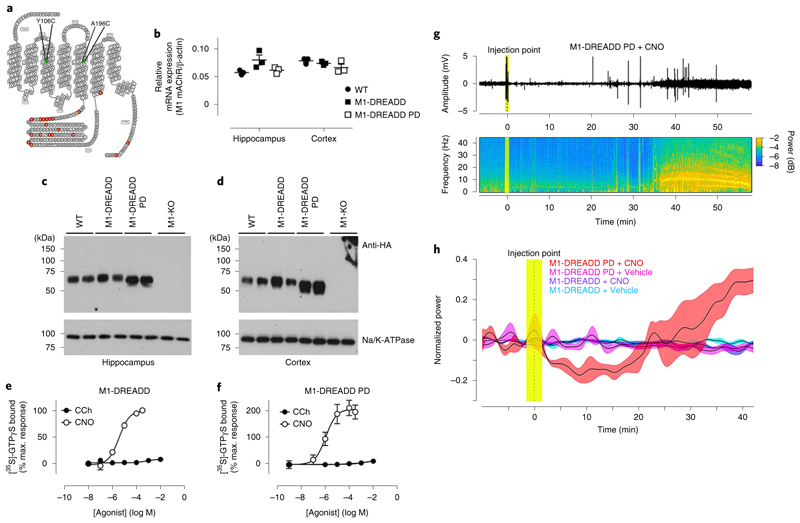
Fig. 5. M1-DREADD PD mice show epileptic-like seizures.
a, Snake plot of the M1 mAChR identifying the mutations introduced to generate the M1-DREADD PD receptor. b, qRT–PCR showing the transcription of M1 mAChR RNA in the hippocampus or cortex of WT, M1-DREADD or M1-DREADD PD mice. Data are expressed as a ratio of β-actin RNA transcription (n = 3 mice). c,d, Solubilized membranes prepared from the hippocampus (c) or cortex (d) of WT, M1-DREADD, M1-DREADD PD and M1-KO mice were probed in a western blot analysis for the expression of M1 mAChR using an antibody for the HA tag. Data shown are for two separate mice for each genotype. Similar data were obtained on at least two further occasions (Supplementary Fig. 2). Na+K+ATPase expression was used as a loading control. e,f, Stimulation of [35S]-GTPγS binding to cortical membranes prepared from M1-DREADD (e) or M1-DREADD PD (f) mice following stimulation with CCh or CNO. Data are expressed as mean ± s.e.m. of 3–4 independent experiments performed in duplicate and normalized to the maximal response at the WT receptor. g, Raw cortical electroencephalogram (EEG) signals (top) and the spectrogram (bottom) in a representative M1-DREADD PD mouse following administration of CNO (0.3 mg kg−1, i.p.) after 15 min of recording basal cortical activity. h, Normalized EEG power in M1-DREADD or M1-DREADD PD mice treated with vehicle (5% glucose) or CNO (0.3 mg kg−1). Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. of 4–8 individual mice and were analyzed using a repeated measures ANOVA, F(3, 3,119) = 5.53, P = 0.029.