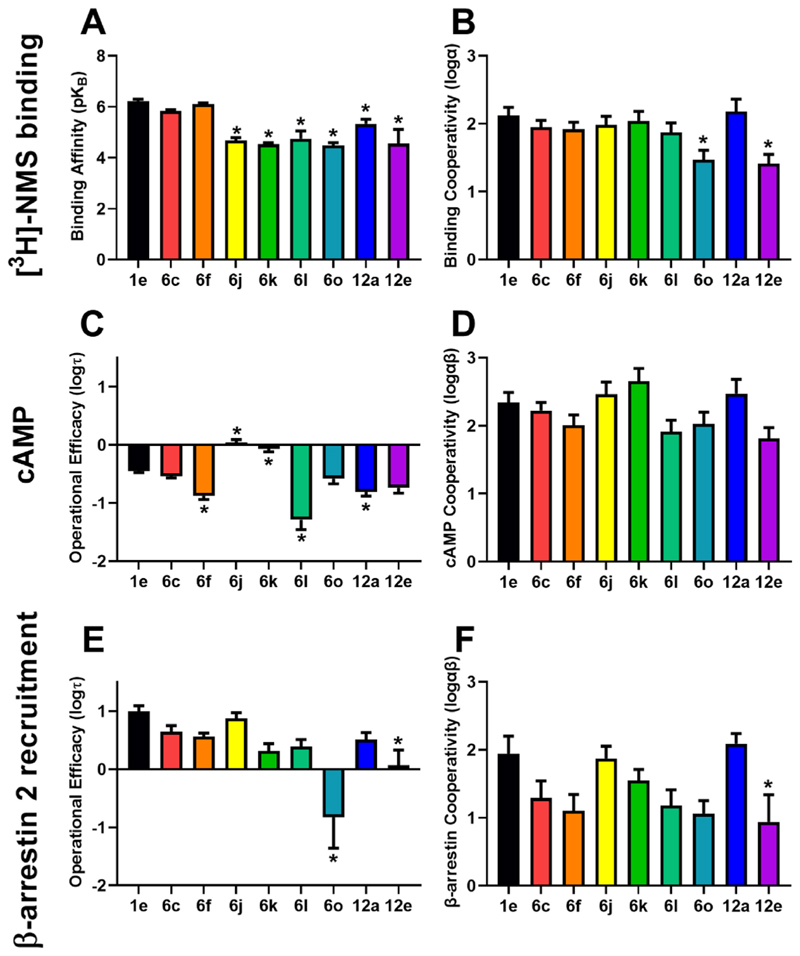
Fig. 3.
Allosteric parameters calculated for 8 novel allosteric modulators. Full allosteric interaction assays (Supp. Fig. 5) were performed using [3H]-N-methyl-scopolamine (NMS) (0.5 nM; 6 h, 23 °C) as the radioligand. ACh competed for binding with [3H]-NMS at the orthosteric site, which was potentiated in the presence of increasing concentrations of each allosteric modulator. (A) Binding affinity (pKB) and (B) binding cooperativity with ACh (log αACh) values were quantified by fitting the data to the allosteric ternary complex model (equation (2) or (4)) [27,28]. The CAMYEL biosensor was used to measure cAMP signalling (5 min, 37 °C) in full allosteric interaction assays (Supp. Fig. 7). (C) Efficacy (log τB) and (D) functional cooperativity with ACh (log αβACh) values were determined by fitting the data to the complete operational model of allosterism and agonism (equation (6)). β-arrestin-eYFP recruitment to the human M4 mAChR-Rluc8 receptor was performed in full allosteric interaction assays (Supp. Fig. 8). (E) Efficacy and (F) functional cooperativity with ACh values were determined by fitting the data to the simplified operational model of allosterism and agonism using equation (7). Data were further analysed by performing one-way ANOVA with a Dunnett post-hoc test to compare the parameters of the novel allosteric modulators with 1e. Data are mean ± SEM of 4–5 independent experiments with repeats in duplicate.