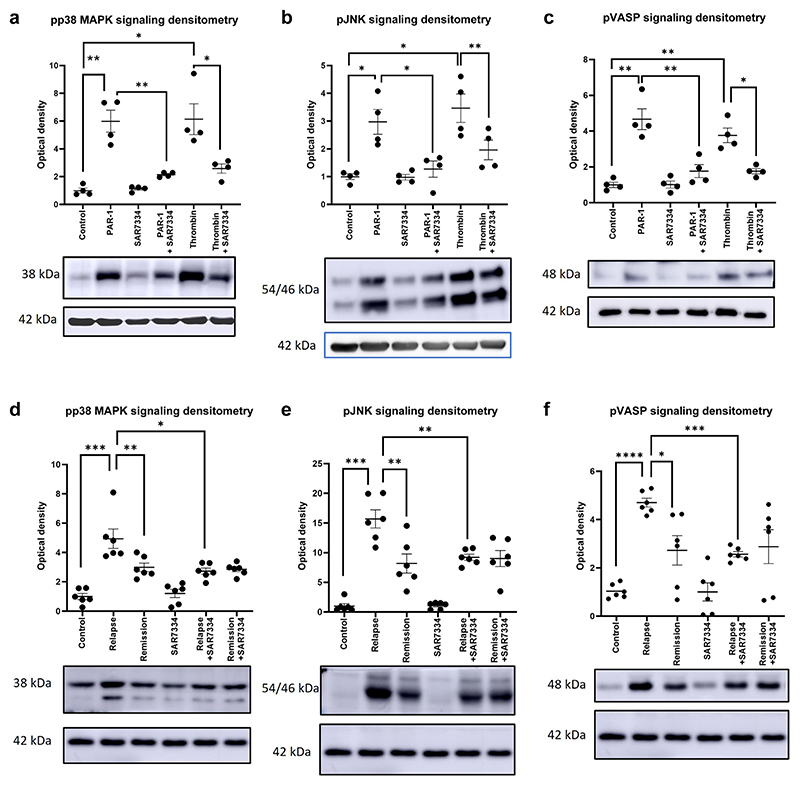
Figure 2. Protease-activated receptor 1 (PAR-1)–associated signaling pathways are activated in human nephrotic syndrome.
PAR-1 agonist treatment at a concentration of 15 μM showed significant stimulation of (a) p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), (b) JNK, and (c) vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) signaling pathways (Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test). The transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily c member 6 (TRPC6) inhibitor SAR7334 (10 nM with 30-minute preincubation) was capable of significantly dampening the response of the podocyte to PAR-1 agonist treatment (a–c) (Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test). Podocytes treated with relapse plasma demonstrated significant stimulation of (d) pp38 MAPK, (e) phospho–c-Jun N-terminal kinase (pJNK), and (f) phospho–vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (pVASP) (Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test) compared with podocytes treated with remission plasma. A further treatment with SAR7334 significantly decreased the stimulation (d–f) (paired 1-way t test). The densitometry shown in (a)–(c) is based on 4 western bots, whereas that shown in (d)–(f) is based on 6, normalized to β-actin load control and relative to control lane. A representative blot is shown beneath each graph. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, and ****P ≤ 0.0001.