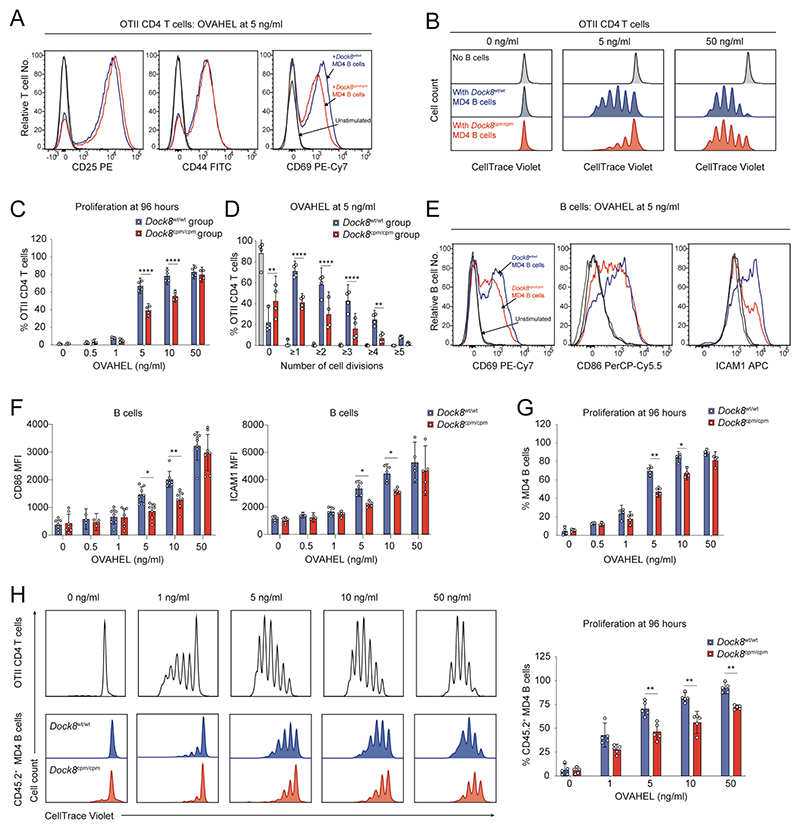
Fig. 5. DOCK8 is required for B and T cell activation when antigen is limiting.
(A) Representative histograms of activation markers at 16 hours and (B) of proliferation at 96 hours for WT OTII CD4 T cells cultured with Dock8wt/wt or Dock8cpm/cpm MD4 splenic B cells at indicated levels of OVAHEL. (C) Proliferation of WT OTII CD4 T cells at indicated levels of OVAHEL and (D) proportion of T cells that have undergone indicated number of cell divisions with 5 ng/ml of OVAHEL at 96 hours. (E) Representative histograms and (F) expression levels of activation markers at 16 hours, and (G) proliferation at 96 hours of Dock8wt/wt or Dock8cpm/cpm MD4 splenic B cells cultured with WT OTII CD4 T cells at indicated levels of OVAHEL. Data in (A, B and E) are representative of four independent experiments. Data in (C, D, F, and G) are pooled from four independent experiments. (H) Representative histograms (left) and pooled data (right) for proliferation of OTII CD4 T cells and CD45.2+ MD4 B cells at 96 hours in mixed cultures of WT OTII CD4 T cells, CD45.1+ Dock8wt/wt and CD45.2+ Dock8wt/wt or Dock8cpm/cpm MD4 splenic B cells at indicated levels of OVAHEL. Data are pooled from five independent experiments. Bars show means, symbols indicate data from individual experiments and error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test (C and D) and by unpaired Welch’s t tests corrected for multiple comparisons using the Holm–Šídák method (F to H) with *P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ****P <0.0001.