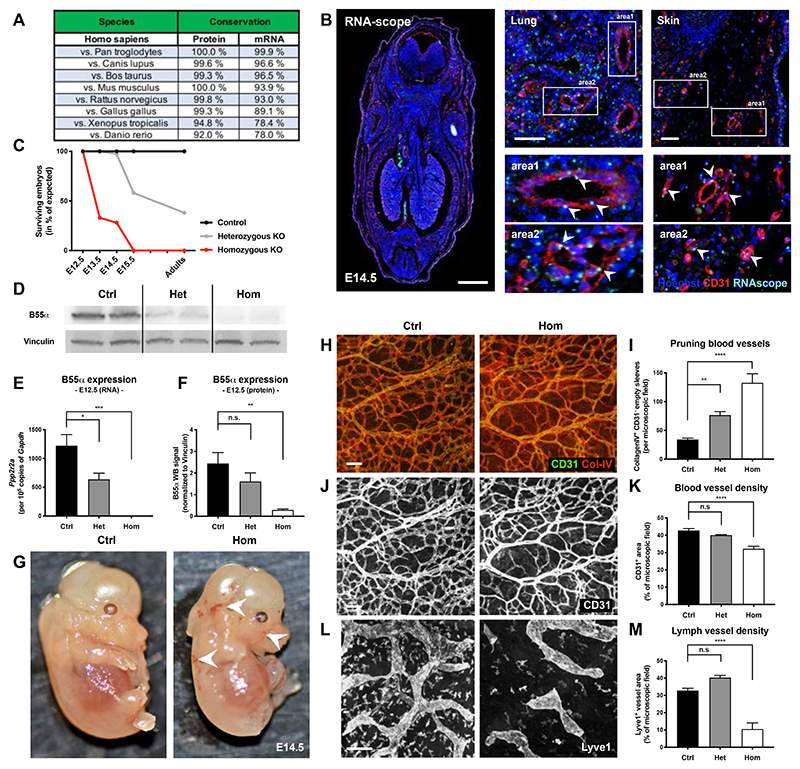
Figure 1. B55α is highly conserved among species and plays an essential role during embryonic development.
(A) Analysis of B55α protein and mRNA sequences showing a high conservation between species.
(B) Expression of B55α in embryonic tissue at day 14.5 post fertilization (=E14.5) assessed by RNAscope (scale bars: 1000µm in overview and 50µm in smaller images).
(C) Ratio of surviving embryos at different stages during development in percent of the expected Mendelian ratio.
(D) Western Blot analysis of tissue samples from control, heterozygous and homozygous KO embryos at E12.5.
(E) Quantitative analysis of B55α RNA levels using qPCR in control, heterozygous and homozygous KO embryos at E12.5 (n ≥ 4 embryos per group)
(F) Quantitative analysis of B55α protein expression in tissue samples from control, heterozygous and homozygous KO embryos at E12.5 (n ≥ 5 embryos per group).
(G) Representative images of surviving littermate controls and Ppp2r2a Full KO embryos at embryonic stage E14.5.
(H,J,L) Representative images of embryonic skin samples from Ppp2r2a KO and littermate controls stained for Collagen IV and CD31+ blood vessels (J) and Lyve1+ lymph vessels (L) (Scale bars: 100 µm).
(I,K,M) Quantitative analysis of Collagen IV+ / CD31- pruning blood vessels (n ≥ 6 per group) (I), CD31+ blood vessel area (n ≥ 3 per group) (K) and Lyve1+ lymph vessel area (n ≥ 4 per group) (M) in surviving embryos at stage E14.5.
P values are *p<0,05; **p<0,001; ***p<0,001; ****p<0,0001.
Graphs show standard error of the mean (SEM).