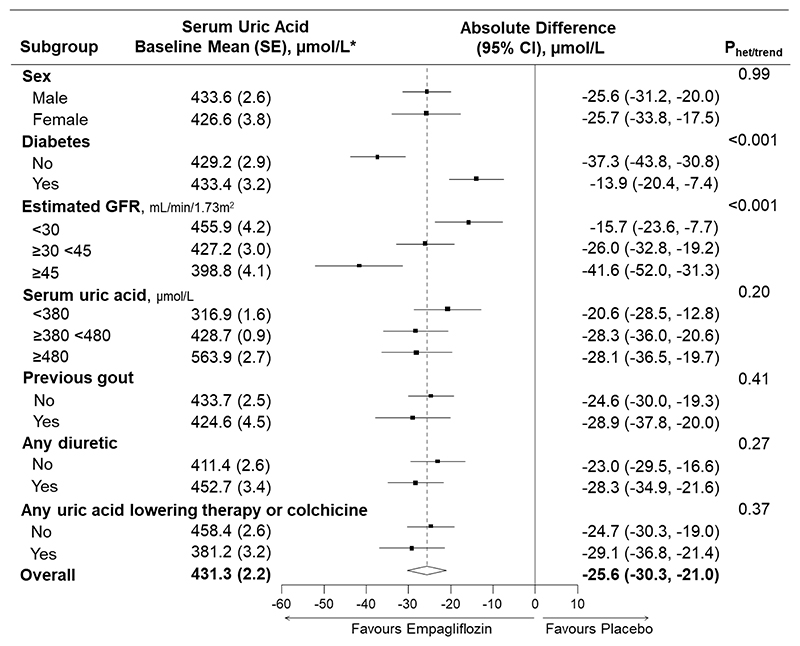
Figure 2. Effects of empagliflozin versus placebo on serum uric acid in subgroups defined by baseline characteristics.
*To convert uric acid to mg/dL, divide by 59.48 (380 μmol/L ≈ 6.4 mg/dL; 480 μmol/L ≈ 8.1 mg/dL). Analysis required participants to have at least one measurement of uric acid during follow-up at 2 and/or 18 months (n=2691 participants). Absolute differences in study-average uric acid between treatment groups (empagliflozin minus placebo) are derived from a repeated measures mixed model (MMRM) adjusted for baseline serum uric acid (in continuous form), baseline-by-time interaction, the covariates used in the minimisation algorithm (categories of age, sex, diabetes, estimated glomerular filtration rate, urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio and region) fixed categorical effects of time, treatment allocation and treatment-by-time interaction, and weighted in proportion to the amount of time between follow-up visits.. Interaction terms are included in the MMRM models to assess for heterogeneity (sex, diabetes, previous gout, any diuretic therapy) between or trend (estimated GFR, serum uric acid) across subgroup-specific means and standard errors. Relative differences are presented in Supplementary Figure 4. Uric-acid lowering therapty includes xanthine oxidase inhibitors and primary uricosuric drugs (see Methods). GFR = glomerular filtration rate. Missing baseline uric acid (4/2691 participants) was imputed with the baseline mean and so participants are included in the middle subgroup category ≥380 <480 μmol/L.