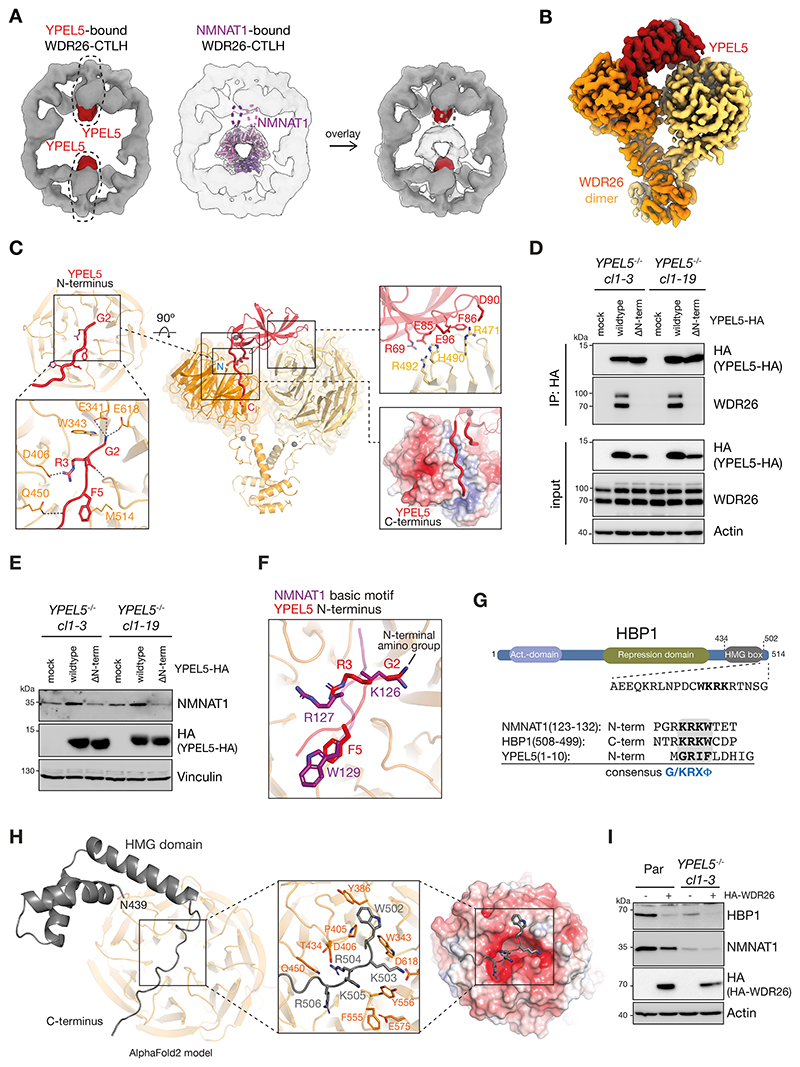
Figure 6. N-terminus of YPEL5 mimics NMNAT1basic degron.
A) Comparison of low-resolution cryo-EM reconstructions of YPEL5-bound (left, YPEL5 shown in red) and NMNAT1-bound (middle, fit with crystal structure of NMNAT1 as in figure 3A, loops highlighted by dotted lines) WDR26-CTLH complex. The overlay of the two maps (right) reveals overlap between YPEL5 and both NMNAT1-binding sites in the opposing WDR26 dimers.
B) Segmented 3.2-Å-resolution focused refined map of YPEL5-bound WDR26 dimer (excluding its CTLH-CRAN domain).
C) Overview of three WDR26-binding elements of YPEL5: 1) residues at the extreme YPEL5 N terminus interacting with the loops surrounding the central pore of WDR26 β-propeller (left); 2) YPEL5 surface encompassing strands and connecting loops from its central β-sheet docked at the side of the second WDR26 β-propeller (right, top); 3) the peptide-like YPEL5 C-terminus interacting with the largely basic groove formed by the blades of WDR26 β-propeller that also binds YPEL5 N terminus (right, bottom).
D) HEK293 YPEL5-/- cells (clones cl1-3 and cl1-19) were mock-transfected or transfected with either C-terminally HA-tagged wildtype YPEL5 or YPEL5 with an N-terminal deletion (ΔN-term). HA-immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblot analysis.
E) HEK293 YPEL5-/- cells (clones cl1-3 and cl1-19) were transfected as in D) and whole cell lysates analyzed by immunoblot analysis. Vinculin detection served as loading control.
F) Overlay of NMNAT1basic and YPEL5 N-terminus bound to WDR26 β-propeller (from AlphaFold2 prediction and cryo-EM structure, respectively).
G) Domain structure of HBP1 indicating activation and repression domains and the High-Mobility-Group (HMG) box (top). HBP1 extreme C-terminal amino acid sequence (aa 502-514) with potential basic motif degron sequence (bold and underlined) aligning with NMNAT1 and YPEL5 binding motifs revealing a consensus sequence (ϕ represents amino acids with a bulky hydrophobic residue including W, Y, F).
H) AlphaFold2 model of HBP1 C-terminus (aa 439-510) binding to WDR26 β-propeller. Close-up shows the disordered region of HBP1 (downstream of its HMG box) interacting with the central negatively-charged pocket of WDR26 β-propeller (bottom, left) mediated by the WDR26-binding consensus basic motif.
I) HEK293 parental and YPEL5-/- knockout cells were either mock-treated or transfected with C-terminal HA-tagged WDR26 and cell lysates analyzed by immunoblot.