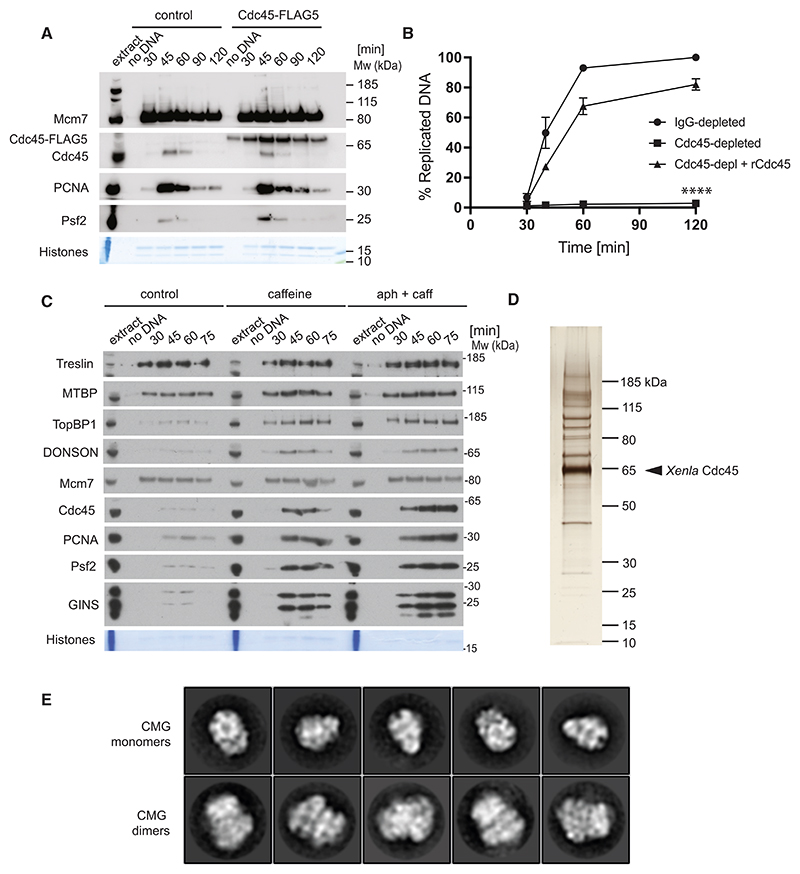
Figure 1. Isolation of replication complexes from chromatin replicated in Xenopus laevis egg extract.
(A). Cdc45-TEV-His10-FLAG5 becomes chromatin incorporated. DNA replication reaction was set up in Xenopus egg extract with optional addition of 70 nM Cdc45-TEV-His10-FLAG5, and chromatin was isolated at indicated times. Chromatin-bound factors were resolved on SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with indicated antibodies. ‘No DNA’ control served as chromatin specificity control, whereas Coomassie stained histones serve as a loading and purity control.
(B). DNA replication reaction was set up in IgG-or Cdc45-depleted extract optionally supplemented with recombinant Cdc45-TEV-His10-FLAG5 as in (A). The synthesis of nascent DNA was followed by incorporation of α32P-dATP into newly synthesized DNA. n = 3, mean with SEM presented. Two-way ANOVA comparing to IgG-depleted, **** p < 0.0001.
(C). DNA replication reaction was set up in Xenopus egg extract with optional addition of 5 mM caffeine and 40 µM aphidicolin. Chromatin was isolated at indicated times and analyzed as in (A).
(D). DNA replication reaction was set up in Xenopus egg extract with optional addition of 70 nM Cdc45-TEV-His10-FLAG5, 5 mM caffeine and 40 µM aphidicolin. After 60 min of the reaction, chromatin was isolated, digested with benzonase, and Cdc45-TEV-His10-FLAG5 immunoprecipitated with M2 FLAG beads. The immunoprecipitated sample was resolved on SDS-PAGE and silver stained.
(E). Negative stain 2D averages of single (first row) and double CMG (second row).