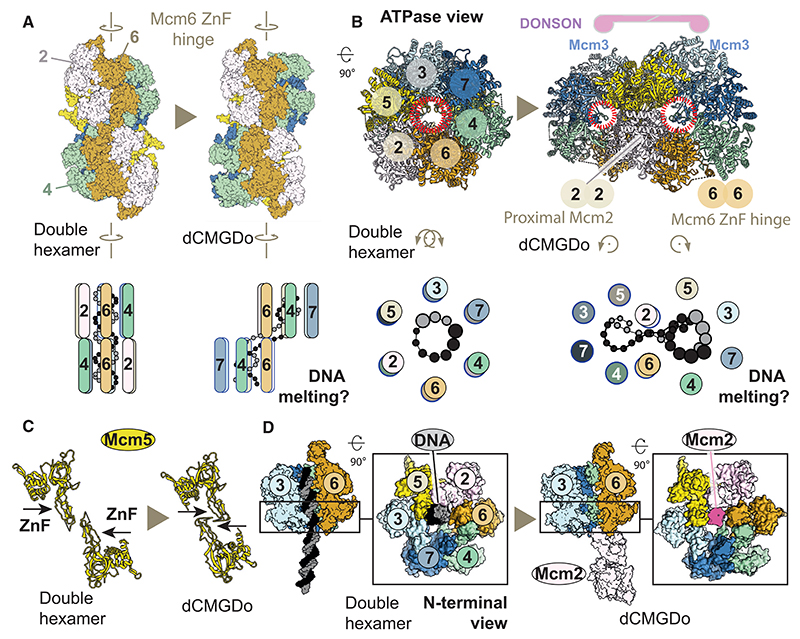
Figure 5. Conformational changes within the MCM occurring upon conversion from double hexamer to dCMGDo.
(A) Two MCM rings, viewed from the side, rotate clockwise with respect to one another pivoting around Mcm6. This movement causes the Mcm7 side of the ring to swing out. This movement agrees with a theoretical model proposed previously.49
(B) The double hexamer to dCMGDo conversion viewed from an end-on view of the ATPase ring. The two MCM central channels are no longer co-axial in dCMGDo.
(C) Two N-terminal ZnF domains cross paths upon conversion from double hexamer to dCMGDo.
(D) Reconfiguration of the N-terminal MCM ring pore upon double hexamer to dCMGDo transition. Mcm2 from one ring in dCMGDo occludes the MCM central channel occupied by duplex DNA in the double hexamer.