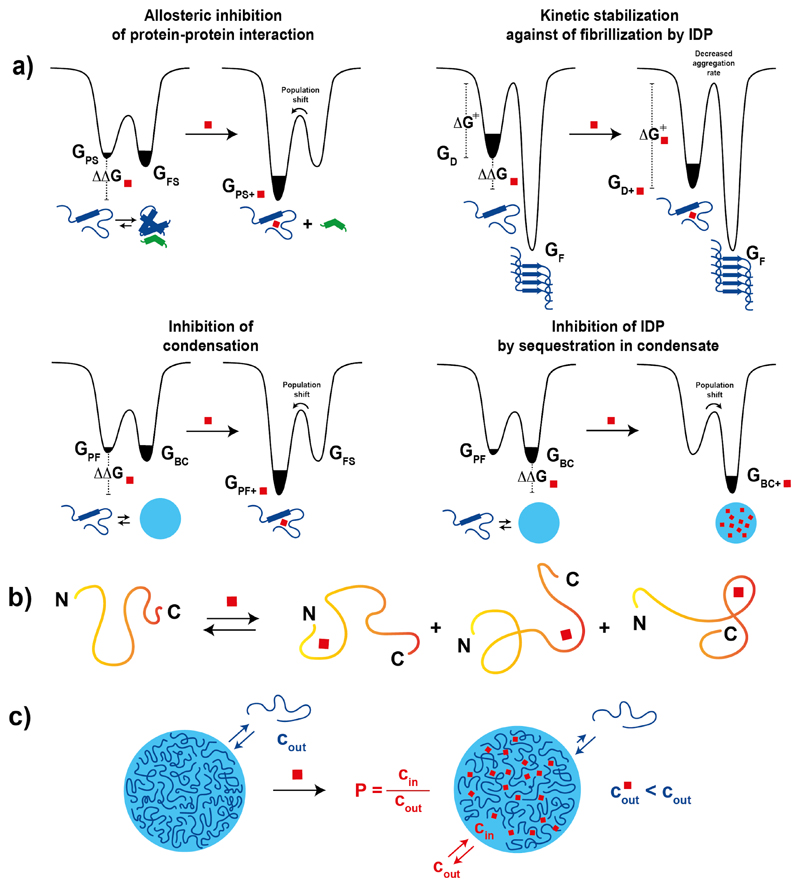
Figure 2.
a) Energy landscape of an intrinsically disordered protein before and after small molecule binding illustrating how it can inhibit protein-protein interactions, provide kinetic stability against fibril formation as well as cause population shifts that promote or suppress biomolecular condensation. b) Schematic illustration of a generalized mechanism for the interaction between small molecules and intrinsically disordered proteins derived from both experimental and computational studies. c) Schematic representation of a biomolecular condensate, of the exchange of protein molecules from the biomolecular condensate to the surrounding solution and of the effect of small molecule binding to an intrinsically disordered protein undergoing biomolecular condensation according to the polyphasic linkage framework.