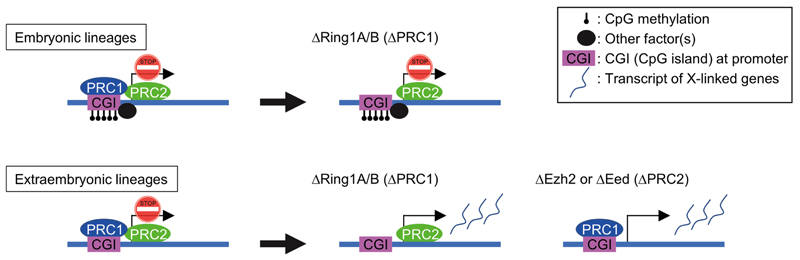
Extended Data Fig. 6. A model for the role of Polycomb complexes in the maintenance of XCI.
(Left) X-linked genes in embryonic and extraembryonic lineages on the Xi are silenced by XCI. CGIs on the Xi are heavily methylated in embryonic lineages, but maintained as hypo-methylated in extraembryonic lineages. (Middle) Ring1A/B knockout resulted in a depletion of all PRC1 subcomplexes on the Xi, but PRC2 is still retained on the Xi, at least in extraembryonic lineages. In this situation, PRC2 accumulation on the Xi is retained at E7.5 but lost at E8.5 in embryonic lineages (here E7.5 is shown). (Right) Ezh2 or Eed knockout resulted in a depletion of PRC2 on the Xi, but PRC1 is still retained on the Xi, in extraembryonic lineages. (Middle and Right) In these situations, many of X-linked genes undergo robust reactivation from the Xi only in extraembryonic lineages. In embryonic lineages, however, X-linked genes are still silenced in the absence of PRC1 or PRC2. DNA methylation of CGIs and/or some other factor(s) might compensate a lack of PRC1 or PRC2 to secure a tight silencing of X-linked genes on the Xi in embryonic lineages.