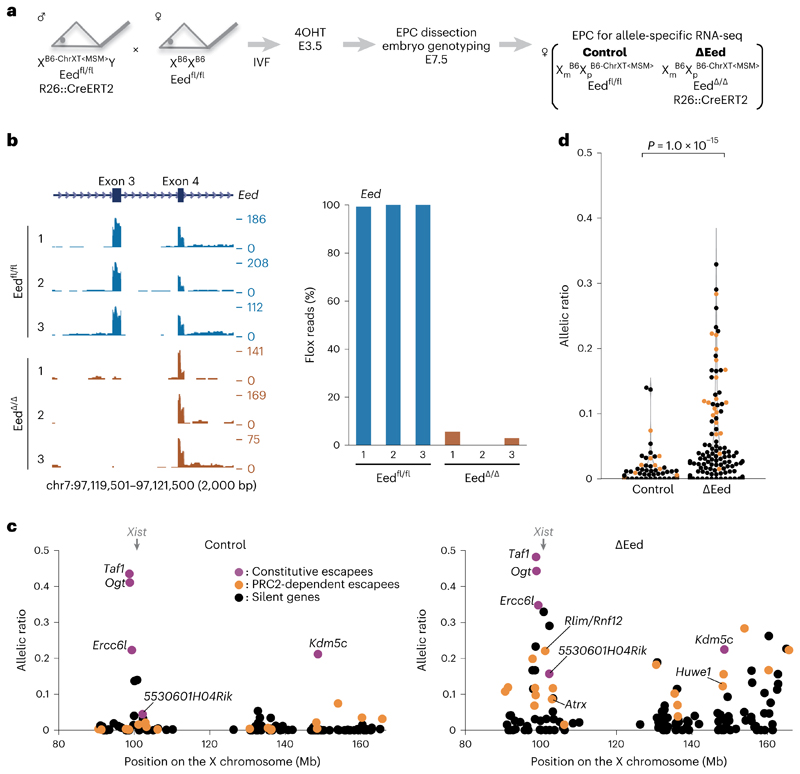
Fig. 5. Deletion of Eed (PRC2) results in loss of chromosome-wide gene silencing on the Xi in EPC.
a Schematic of allele-specific RNA-seq using ÄEed conditional knockout mouse. Embryos were recovered at E7.5 after 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4OHT) treatment of blastocysts obtained from in vitro fertilization (IVF) at E3.5 (Methods). EPC was isolated and applied for RNA-seq library preparation. b, Genome browser plots showing allele-specific RNA-seq reads of three controls and three ÄEed EPCs at Eed locus. The third coding exon is deleted upon CreERT2 activation. c, Allele-specific RNA-seq shows chromosomewide gene escape from XCI upon PRC2 deletion. A total of 132 informative genes including Xist and 5 constitutive escapees (magenta), 19 significant escapees upon PRC2 deletion (orange) and 107 silenced genes even in the absence of PRC2 (black) are shown in both control and ÄEed EPCs. Average of three independent EPCs. P values were calculated using one-sided Student’s t-test, and each P value is shown in Supplementary Table 3. d, Total change of allelic ratio upon PRC2 deletion. Allelic ratios of each X-linked gene in control and ÄEed E7.5 EPCs. A total of 126 informative genes including 19 significant escapees upon PRC2 deletion (orange) and 107 silenced genes even in the absence of PRC2 (black) are shown in both control and ÄEed EPCs. P values were calculated using one-sided Brunner–Munzel test.