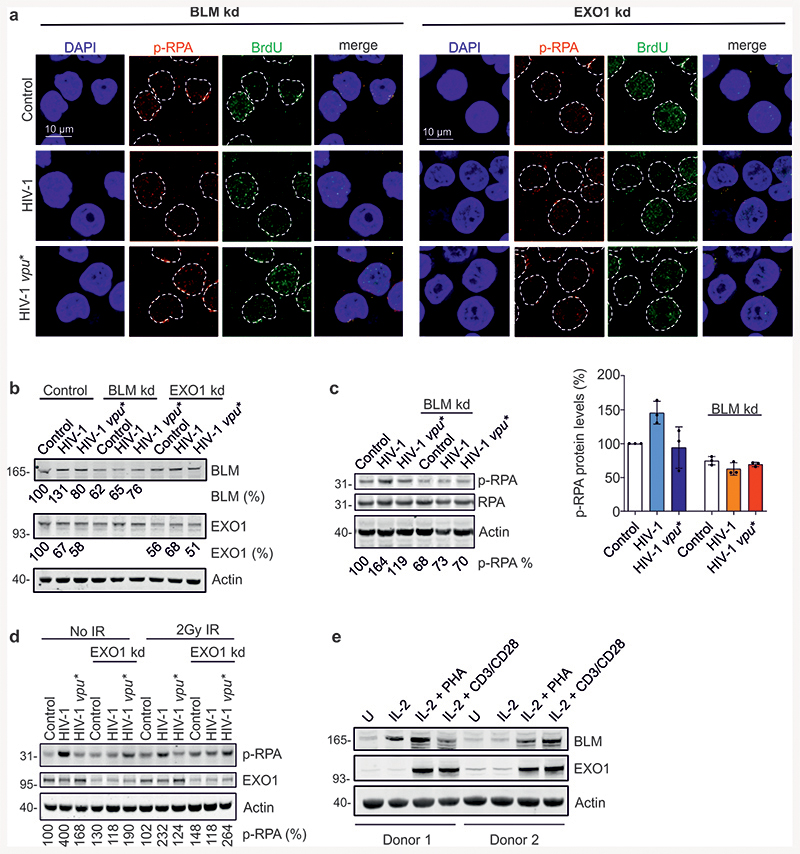
Extended Data Fig. 5. Role of BLM and EXO1 in Vpu-mediated modulation of DNA end processing.
Role of BLM and EXO1 in Vpu-mediated modulation of DNA end processing. (a) Representative images for immunofluorescence analysis of p-RPA and BrdU and (b) knock-down efficiency of BLM and EXO1. (c) p-RPA accumulation as a function of BLM. WTK1(HR/3’) cells were γ-irradiated (2Gy) 48h after transfection with wt or vpu* pHIV-1-NL4-3-env*-IRES-mCherry plus shRNA to silence BLM (BLMkd). 1h post-irradiation, samples were taken for p-RPA32 S4/8 and RPA Western Blot analysis. The right panel shows mean values (±SD) of p-RPA levels obtained in three independent experiments relative to control cells. (d) p-RPA Western blot analysis in WTK1(HR/3’) cells transfected with wt or vpu* pHIV-1-NL4-3-env*-IRES-mCherry, together with shRNA against EXO1. 48 h after transfection cells were irradiated and taken for Western blotting. (e) Expression of BLM and EXO1 in primary CD4+ T cells. CD4+ T cells isolated form two blood donors were either treated with IL-2 alone or stimulated with IL-2/PHA or IL-2 and CD3/CD28 magnetic beads or left untreated (U) for 3d when cells were harvested for Western blot analysis.