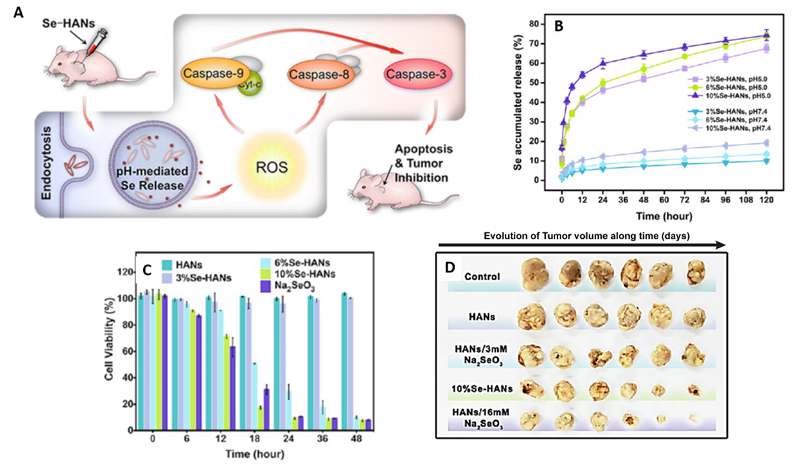
Figure 7.
(A) In vivo treatment of mice-bearing osteosarcoma with pH-responsive release of selenium-doped hydroxyapatite nanoparticles (Se-HANs) HANs. Internalized Se-HANs by nonspecific endocytosis are rapidly degraded in acidic lysosomes to release selenium. (B) Selenium release from Se-HANs exhibited a pH-responsive release profile at pH = 5.0 versus pH = 7.4. (C) CCK-8 assay of MNNG/HOS osteosarcoma cells showed that viability was highly associated with selenium content and degradation of Se-HANs. (D) In vivo evaluation of anti-osteosarcoma activity of Se-HANs after intratumoral injection on a xenograft osteosarcoma model. Compounds with higher selenium content, including 10%Se-HANs and HANs/16 mM Na2SeO3 exhibited efficient inhibition of tumor growth as evidenced by the reduction of tumor size (left). Adapted from [112] with permission from the American Chemical Society.