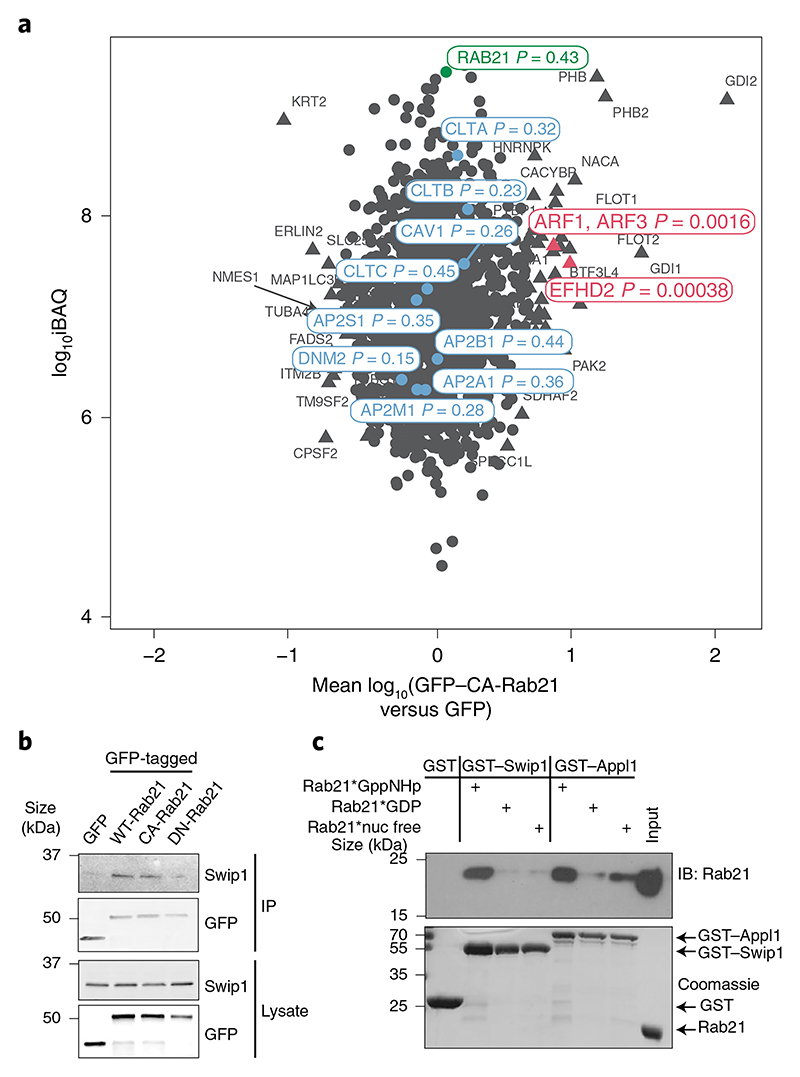
Fig. 1. Swip1 interacts directly with active Rab21.
a, SILAC proteomics analysis of GFP-Trap pulldowns in MDA-MB-231 cells expressing GFP-tagged CA-Rab21 versus GFP alone. The plot is representative of two independent experiments, forward and reverse; the experiments consisted of two independent affinity purifications. The plot shows the mean fold-changes from the forward and reverse experiments against absolute protein abundances (intensity-based absolute quantification, iBAQ). Abundance bins were defined by including 1,000 proteins in a subsequent order. The log10-transformed fold-change values of the proteins were tested for statistical significance using double-sided Significance B tests. No multiple hypothesis correction method was applied due to the small number of selected proteins for the statistical analysis. Proteins with P < 0.01 are represented by a triangle and non-significant proteins are shown as circles. P values are depicted in the figure for a selected set of proteins. The proteins in red are markedly enriched in the CA-Rab21 fraction and proteins in blue are known endosomal proteins—clathrin (CLTA, CLTB and CLTC), AP2 (AP2A1, AP2B1, AP2M1 and AP2S1), caveolin (CAV1) and dynamin II (DNM2)—that are not specifically enriched. b, Representative immunoblots of GFP-Trap pulldowns from MDA-MB-231 cells transfected with the indicated constructs and probed for GFP and endogenous Swip1. Three independent experiments were performed. GFP–DN-Rab21, Rab21T33N dominant negative, GDP-bound/nucleotide-free; IP, immunoprecipitation. c, Coomassie-stained gel and immunoblot (IB) of GST-pulldowns with the indicated GST-tagged proteins and recombinant Rab21 (indicated by asterisks) bound to a non-hydrolysable form of GTP (GppNHP; active Rab21), GDP or no nucleotide after EDTA treatment (nuc free). The Rab21-effector GST–APPL1 was used as a positive control. Three independent experiments were performed. Unprocessed blots are provided.