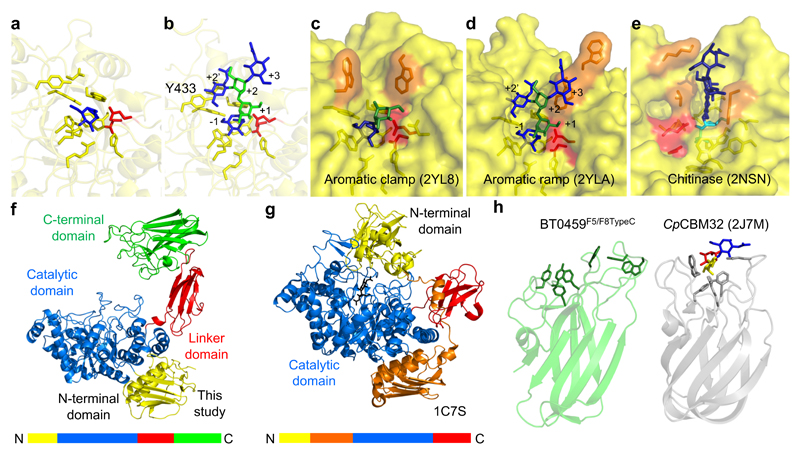
Figure 6. Crystal structure of BT0459GH20.
a, A close up of the active site of BT0459GH20 with the residues forming the -1 subsite shown as sticks and a GlcNAc (blue) product in the active site. b, A close up of the active site of BT0459GH20 overlaid with a CNG structure (from 2YLA). Mannose and GlcNAc are green and blue, respectively, with the antennary GlcNAc in the active site. The α1,3 mannose arm is in the +1 position and the core mannose and GlcNAc occupy the +2 and +3 subsites, respectively. A clash can be seen between the Y433 and the bisecting GlcNAc in the +2’ position. The active sites of the S. pneumonie c, SpGH20A and d, SpGH20B, and e, a GH20 active on chitooligosaccharides from O. furnacalis. The inhibitor in e is TMG-chitotriomycin (TMG and GlcNAcs shown in cyan and dark blue, respectively). Catalytic residues are shown in red and those residues interacting with sugars in the positive subsites are in orange. f, The full length structure of BT0459GH20 and g, the S. marcescens GH20 (1C7S). The order of the modules are shown as coloured bars. h, The C-terminal F5/F8 type C domain of BT0459GH20 is shown (BT0459F5/F8TypeC, left) and aromatic residues on the potential glycan binding surface are shown as sticks. A structural homologue of BT0459F5/F8TypeC is shown for comparison (right) and is a CBM32 from a C. perfringens GH84 (CpCBM32). This has a trisaccharide ligand of fucose, galactose and GlcNAc (red, yellow and blue, respectively) bound and the aromatic residues involved in binding are shown as sticks. The core folds between BT0459F5/F8TypeC and CpCBM32 are very similar but the potential glycan binding surfaces vary greatly (see Supplementary Fig. 12 for further structural homologues).