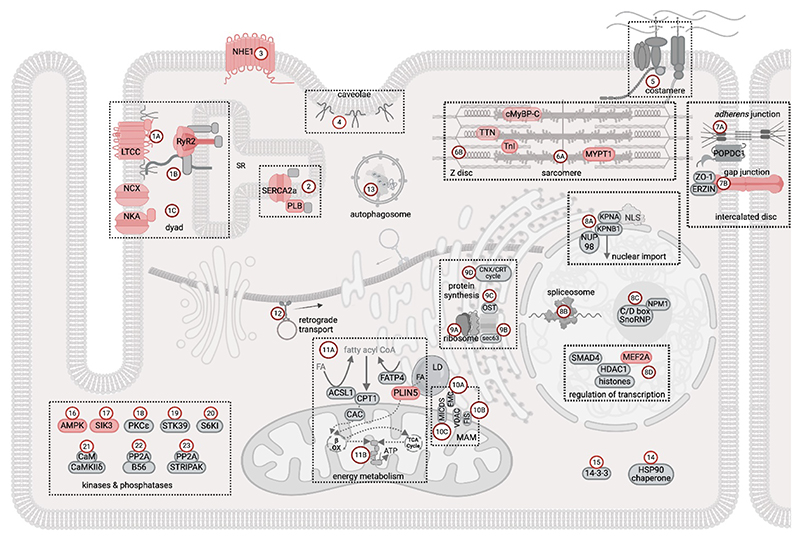
Figure 8. Map of the PDE3A1-dependent cAMP nanodomains in rat cardiac myocytes.
The cartoon shows the PDE3A1-dependent cAMP nanodomains distributed across various subcellular structures. This depiction is based on data obtained by the integrated STRING network analysis of two orthogonal datasets − the PDE3A1 interactome and the PDE3-dependent phosphoproteome − generated by mass spectrometry analysis of rat cardiac myocyte samples stimulated with isoproterenol (232). The output of this analysis is multiple protein interaction subnetworks, or modulomes, each including one or more PDE3A1 interactors and one or more phosphotargets. Each subnetwork is given a number and a letter following the number denotes subnetworks that can be grouped within a certain location or are involved in the same functional activity. Previously known PKA targets identified in this study are highlighted in red. The protein components for each group, identified by their gene name, are listed below. Interactors are in bold, phosphotargets are underscored.
1: dyad − includes the L-type calcium channel (LTCC) modulome (1A; CACNA1C, CACNB2, AHNAK), the RyR2 modulome (1B; ASPH, CASQ2, JPH2, HRC, RYR2, SPEG) and the Na+, K+-ATPase (NKA) and Na+, Ca2+ exchanger or NCX modulome (1C; ATP1A1, ATP1B1, and SLC8A1).
2: SERCA2a (sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum calcium-ATPase) modulome, (ATP2A2, HAX1, PLN, SRL). Involvement of PDE3A in this complex had been previously reported (80, 81).
3: Na+, H+ exchanger NHE1 modulome (SLC9A1), also previously reported (531).
4: caveolae modulome (CAV1, CAV2, CAV3, CAVIN 1).
5: costamere modulome (ITGB1, LAMB1, LAMB2, LAMC1, DMD, SGCA, SNTB1).
6: sarcomere - comprises myofibril modulome (6A; MYH6, MYH7, MYL2, MYL3, TTN, LMOD2, MYBPC3, PPP1R12A, TNNI3) and Z disc modulome (6B; ACTN1, ACTN2, ACTN4, DES, FLNC, MYOZ2, OBSCN).
7: intercalated disc, comprises adherens junction modulome (7A; CTNNB1, MYZAP, XIRP1, BVES (POPDC1), CTNNA1, CTNNA3, CXADR, TJP1, XIRP2) and gap junction modulome (7B; EZR (erzin), GJA1 (Cx43), TJP1 (ZO-1)).
8: nucleus, comprises nuclear transport machinery modulome (8A; KPNA1, KPNA2, KPNB1, KPNA3, NUP98), spliceosome modulome (8B; DHX9, EFTUD2, HNRNPA0, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPAB, HNRNPC, HNRNPM, HNRNPU, LUC7L2, MATR3, PRPF8, RBMX, SNRPF, U2AF2, SRSF3, SRSF7, YBX1, PRPF31, RBM20, SERBP1, SF1, SRPK1, SRPK3, SRRM1, THRAP3, ZRANB2), nucleolus modulome (8C; FBL and NOP58 of C/D box SnoRNP and NPM1), and a modulome including proteins that regulate gene expression (8C; SMAD4, HDAC1, MEF2A, together with histones H1, H2A, H2B, H3, H4).
9: protein synthesis machineries at the ER, including ribosomal proteins modulome (9A; RPL3-6, 7a, 9, 12-15, 18, 19, 22, 23a, 32, 35a, RPLP0, RPLP2, RPS14, 18, 26, 27l, EEF1B2, EIF3A, EIF3C, EIF3G, EIF3S6IP, ABCF1, EEF1D, EIF4EBP1, EIF4G1, EIF5B, NACA), transport into the ER modulome (9B; SEC63, HSPA5), N-linked glycosylation oligosaccharyl-transferase complex, or OST, modulome (9C; DDOST, RPN1, RPN2, STT3A, STT3B), and ER chaperone system for glycoproteins or calnexin-calreticulin (CNX-CRT) cycle modulome (9D; CANX, CAL).
10: mitochondria-associated membrane (MAM), including ER membrane complex (EMC) modulome (10A; EMC1, EMC2, EMC3, EMC10) and (10B; FIS1, VDAC1, VDAC2) and MICOS-MIB (mitochondrial contact site - mitochondrial intermembrane space bridging) modulome (10C; APOOL, CHCHD3, IMMT, RHOT2, SAMM50).
11: energy metabolism regulation, including fatty acid mitochondria uptake modulome (11A; CPT1A, CPT1B, SLC27A4 (FATP4), SLC25A20 (CAC), ACSL1, and lipid droplet (LD) protein, PLIN5) and electron transport chain (11B, ATP5F1A, ATP5F1B-D, ATP5PB, ATP5PD, ATP5MG, ATP5PO, ATP5PF, COX15, COX5B, MT-CO2, COX10, NDUFA13, NDUFA9, NDUFS7-8, UQCRQ, UQCRC1, UQCRH).
12: retrograde transport (DCTN2 and DYNC1LI1).
13 autophagosome, comprising the chaperone-assisted selective autophagy (CASA) complex (BAG3, HSPA8, HSPB8) and cargo protein SQSTM1.
14: HSP90 chaperone (CDC37, HSP90AA1, HSPA1A)
15: 14-3-3 scaffold proteins (YWHAB, YWHAG, YWHAH, YWHAQ), which are known interactors of PDE3A (82).
16 -21: kinases, including AMPK (16; PRKAA2, PRKAB1), SIK3 (17), PKC (18; PRKCE), STK39 (19), S6KI (20; RPS6KB1), Ca2+/calmodulin (CaM)-dependent protein kinase (CaMK) II delta (21; CALM1, CAMK2D).
22-23: protein phosphatase 2 (PP2) complexes, (22; PPP2R1A and PPP2R5A) (previously reported (532) and PP2A-STRIPAK (23; PPP2R1A, SLMAP, STRN, STRN3, STRN4).
This figure was generated using Biorender.