Figure 4.
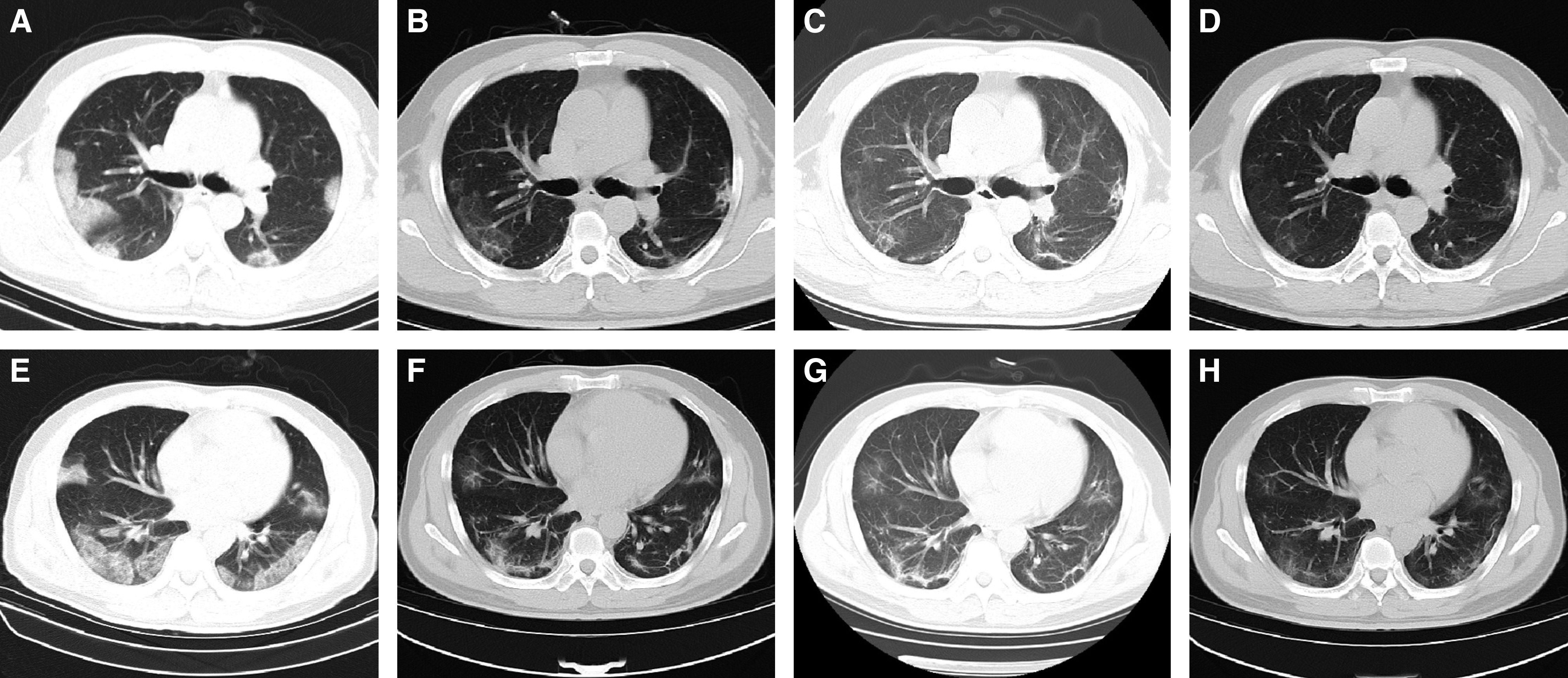
The chest computed tomographic (CT) scans from a 48-year-old male patient with coronavirus disease (COVID-19). (A and E) The chest CT scans at admission. Multiple patchy ground-glass opacities (GGOs), consolidation, and interlobular septal thickening were shown in the lower lobes. (B and F) The last chest CT scans before discharge. Most of the subpleural consolidations were absorbed. Small patchy consolidation in the lower right lung was present. GGOs transformed into irregular lines and subpleural lines. The density of the interlobular septal thickening decreased. (C and G) The chest CT scans 2 weeks after discharge. The consolidation in the right lower lobe transformed into GGO. The density of subpleural GGO in both lungs was gradually absorbed. (D and H) The chest CT scans 4 weeks after discharge show that the damage was partly absorbed. The consolidation in the left upper lobe transformed into GGO, and the subpleural GGO was further absorbed.
