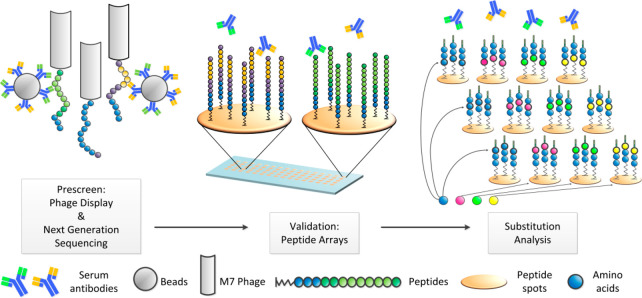
Figure 5.
In an initial prescreen, up to 109 random peptides displayed on phage were screened for their binding to serum antibodies, immobilized on beads. Next, the identified epitope peptides were validated with solid material-based peptide microarray technology. Finally, the validated epitopes were fine mapped by comprehensive substitution analysis. The resulting “binding fingerprints” enable the identification of those proteins that match the antibody specificity, and, eventually, the correlation to disease causing agents. Reprinted with permission from ref (146). Copyright 2017 Elsevier B.V.