Figure 4. Sevoflurane interaction with TLR2.
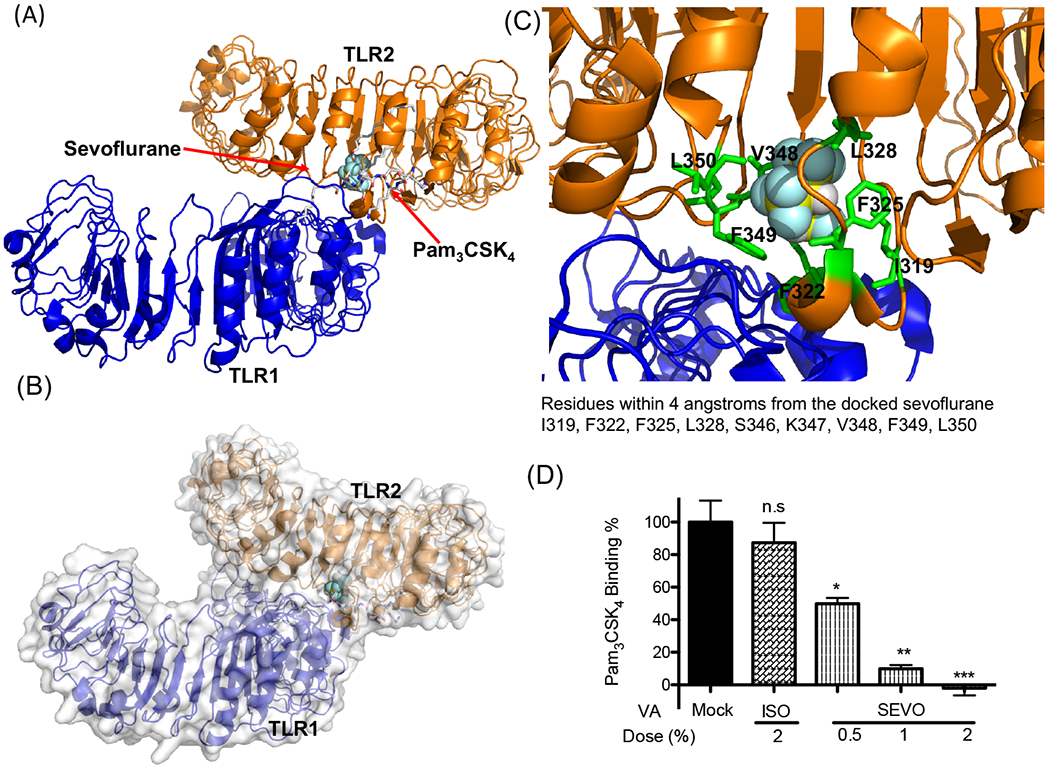
(A, B, C) Rigid docking simulation was performed to predict sevoflurane binding on TLR1/TLR2. Sevoflurane bound to the internal pocket on TLR2 that Pam3CSK4 binds to (A, B). Blow-out image of the sevoflurane binding site. The nearby residues around sevoflurane (within 4 angstroms from the sevoflurane) are shown with sticks.
(D) Pam3CSK4 binding to HEK-TLR2 cells was tested with or without volatile isoflurane or sevoflurane. Data were shown as mean +/− S.D. 6 independent replicates were used per group. Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunns post hoc analysis was performed for statistical analysis. *, **, and *** denote adjusted p< 0.05, 0.01, and 0.001 vs mock, respectively. n.s.; not significant, ISO; isoflurane, SEVO; sevoflurane, VA; volatile anesthetic.
