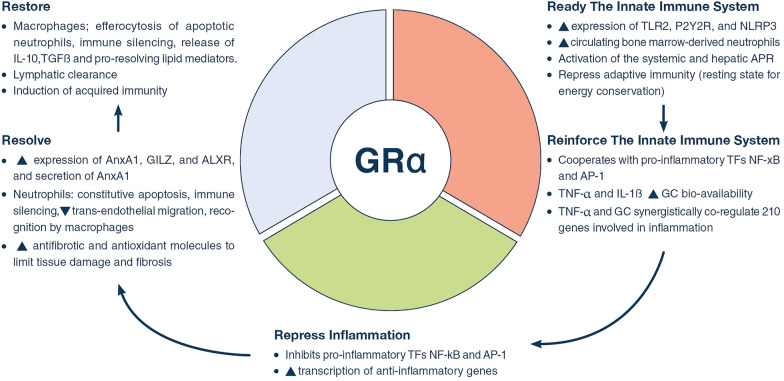
Fig. 2.
Glucocorticoid receptor α as a cellular rheostat of homeostatic corrections. The glucocorticoid receptor α (GRα) acts as a cellular rheostat to ensure that a proper response is elicited by the neuroendocrine and immune systems throughout the three phases of homeostatic corrections. The serial sequence of regulatory functions includes the: (1) activation and reinforcement of innate immunity (ready-reinforce), (2) downregulation of pro-inflammatory transcription factors (repress), and (3) promotion of disease resolution (resolve- restore).by switching production from pro-inflammatory to pro-resolving mediators, while at the same stimulating antifibrotic and antioxidant molecules that limit tissue damage and fibrosis, to help achieve optimal restoration of anatomy and function of the affected tissues, and (4) parallel support of adaptive immunity. Modified with permission from reference.[4]. TLR2 toll-like receptor 2, purinergic receptor P2Y2R; NLRP3 NOD-like receptor pyrin containing 3, APR acute phase response, TF transcription factor, NF-κB nuclear factor-κB, AP-1 activator protein-1, AnxA1 annexinA1, AnxA1 receptor, ALXR A4 lipoxin receptor, GILZ glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper, TGFβ transforming growth factor β