Figure 10.
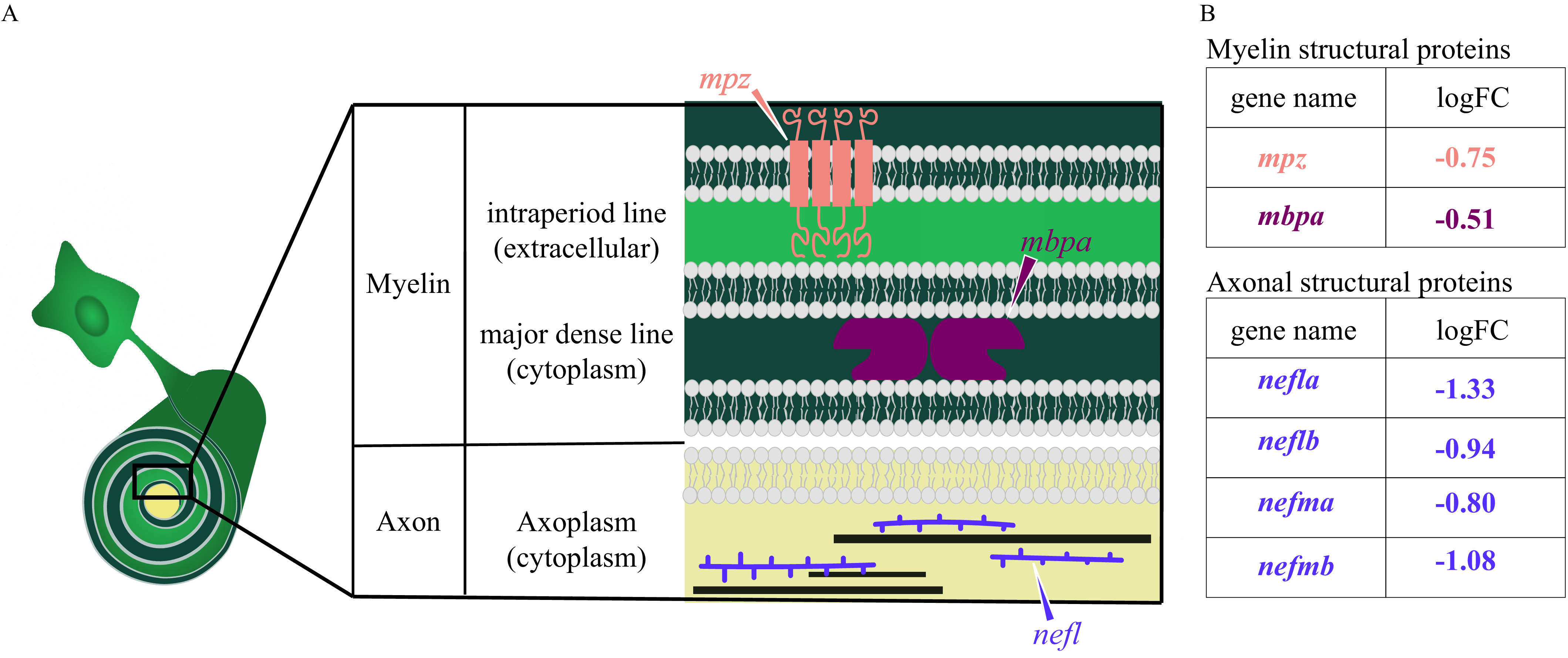
Diagram of myelin and axonal structural proteins differentially expressed in domoic acid (DomA)-exposed fish. (A) Schematic of the cross section of an axon–myelin interface with a focus on selected myelin and axon structural proteins that are differentially expressed in DomA-exposed fish at 3 d postfertilization. The magnified cross section shows the major divisions in myelin (Barkovich 2000): first, major dense line: the electron-dense cytoplasm where myelin basic protein (encoded by the mbp gene) attaches to the inner surface of the membrane proteins and stabilizes myelin, and second, the intraperiod line, the less electron-dense extracellular space. Transmembrane proteins like myelin protein zero (encoded by the mpz gene) maintains compact myelin structure through its cytoplasmic and extracellular interactions. The cross section also shows a simplified axoplasm that contains neurofilaments that form part of the axon cytoskeleton. (B) Myelin and structural proteins that are differentially expressed, with their log fold change (logFC). –, gene was down-regulated in DomA-exposed fish relative to controls.
