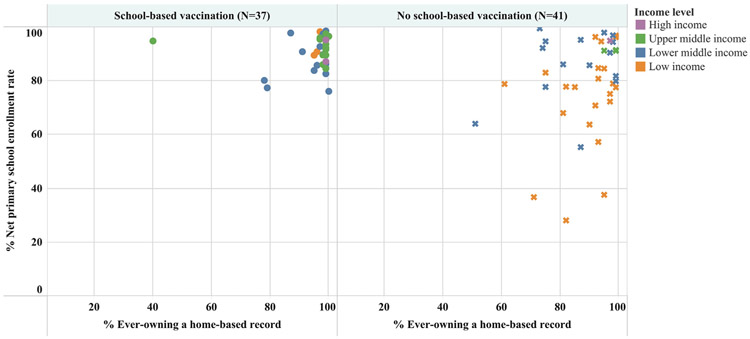
Fig. 5.
Primary school enrollment and home-based record ownership among 78 World Health Organization (WHO) member states reporting delivery of routine doses of vaccines in schools in 2017 in the WHO–United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) Joint Reporting Form that had data available on net primary school enrollment rateb and home-based record ownershipc, by World Bank income level. aSchool-based vaccination is defined as the delivery of routinely recommended doses of vaccines to school-aged children using the school as a venue for delivery (excludes doses given during campaigns). bTotal number of students in theoretical age group for primary education enrolled in that level, divided by the total population in that age group. cThe proportion of children aged 12–23 months who had ever owned a home-based record, according to a country’s most recent MICS or DHS survey data. Note: Countries having both net primary school enrollment rate and % ever owning an HBR ≥ 80% were identified as having the highest potential for delivering school-based vaccination and checking children’s vaccination status at school entry.