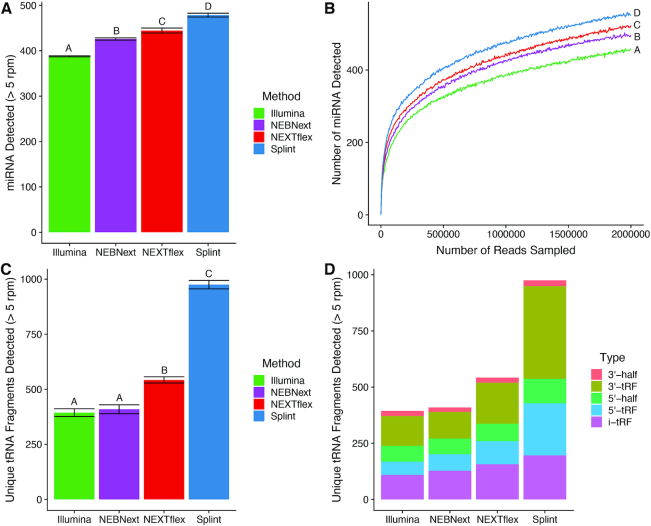
Figure 4.
sRNAs detected in human brain. (A) The number of miRNAs from human brain detected at a threshold of >5 reads per million (rpm), represented as an average of 3–4 technical replicates per method. Error bars represent the standard deviation of the mean and letters represent groups that are significantly different from each other with a Tukey corrected P-value < 0.001. (B) Number of miRNAs detected with a read depth >5 rpm at various subsampled read depths. Datasets were randomly sampled with the number of reads increasing by 5000 in each sample. Values represent the mean number detected in four technical replicates individually sampled at each read depth. Letters represent groups that are significantly different from each other with a Tukey corrected P-value < 0.001 at the 2 million read sampling endpoint. (C) Number of unique and unambiguously identifiable tRNA fragments detected with each method at a threshold of >5 rpm. Values represent the average ± standard deviation of 3–4 technical replicates per method. Letters represent groups that are significantly different from each other with a Tukey corrected P-value < 0.0001. (D) Composition of tRNA fragment categories identified by each method represented as an average of 3–4 technical replicates. Categories were defined as follows: 3′ and 5′ tRNA-haves are fragments that terminate or begin at the known angiogenin cleavage sites and contain the rest of the 5′ or 3′ end of the tRNA. 5′ tRNA fragments (5′-tRFs) begin a the 5′ end of the tRNA but end either before or after the angiogenin cleavage sites. 3′ tRNA fragments (3′-tRFs) begin either before or after the angiogenin cleavage sites and end within the CCA tail of the 3′ terminus of the tRNA. Internal tRNA fragments (i-tRF) are fragments that begin after the 5′ terminus and end before the CCA tail of the 3′ end of the tRNA.