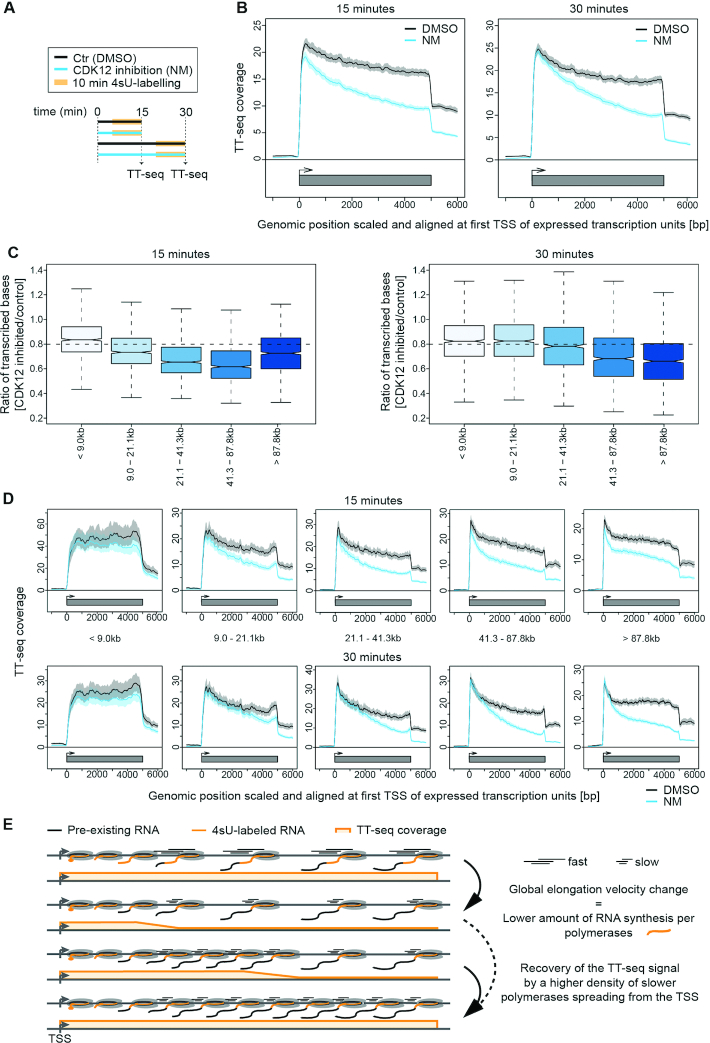
Figure 1.
CDK12as inhibition globally decreases RNA synthesis. (A) Experimental design. (B) Metagene analysis of TT-seq signal for expressed genes after treatment of cells with DMSO (black) versus 7.5 μM NM treatment (blue) for 15 min (left) or 30 min (right). The TT-seq coverage was averaged and aligned at their transcription start sites (TSSs) and polyadenylation (pA)-sites. Shaded areas around the average signal (solid lines) indicate confidential intervals. (C) Box plots of different length classes show the ratio of transcribed bases after 15 min (left) and 30 min (right) inhibition of CDK12as compared to control. (D) Metagene analysis for different length classes comparing the average TT-seq signal before (DMSO treatment, black) and after CDK12as inhibition (7.5 μM NM treatment, blue) for 15 min (upper panel) and 30 min (lower panel). The TT-seq coverage was averaged and aligned at their transcription start sites (TSSs) and polyadenylation (pA)-sites. Shaded areas around the average signal (solid lines) indicate confidential intervals. (E) Schematic representation of TT-seq signal changes along the gene body upon elongation velocity change. Upper panel: steady state transcription. Lower panels show TT-seq signal recovery spreading from the TSS.