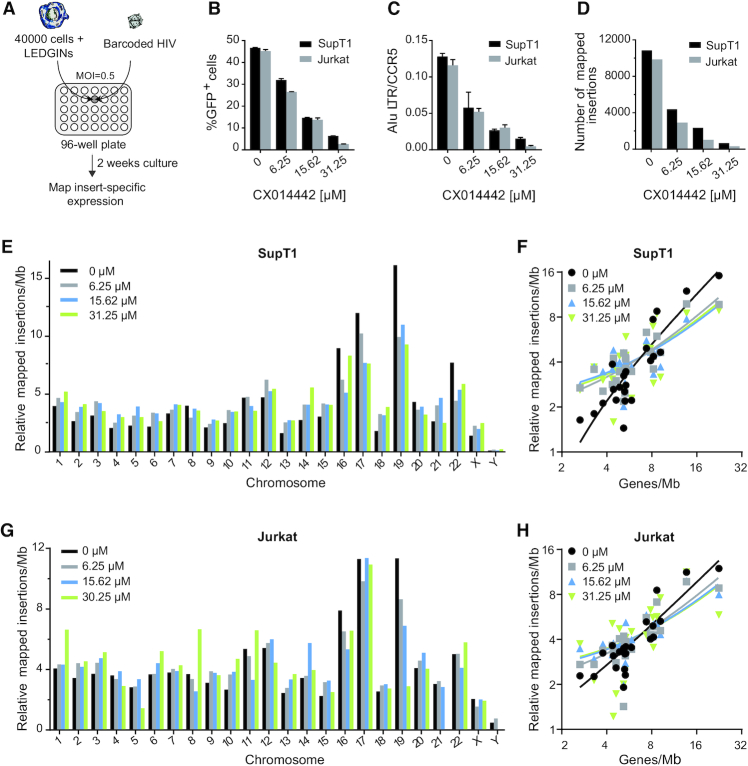
Figure 1.
LEDGINs inhibit integration and reduce chromosomal preference. (A) 40 000 Jurkat or SupT1 cells were transduced in a 96-well plate with barcoded HIV in the presence of varying concentrations of LEDGIN CX014442. Cells were cultured for two weeks before DNA and RNA were extracted. (B) The percentage of GFP positive cells two weeks post transduction of SupT1 (black) and Jurkat (gray) cells in the presence of LEDGIN CX014442. Bars represent the average of flow cytometry measurement in duplicate with standard deviation. (C) The number of integrated copies two weeks post transduction, as determined by Alu-LTR nested qPCR on gDNA that was normalized to CCR5. Bars represent the average of qPCR in duplicate with standard deviation. (D) The number of retrieved integration sites in SupT1 and Jurkat cells. (E, G) Relative number of mapped insertions/Mb plotted for each chromosome in SupT1 (E) and Jukat (G) cells whereby the sum of all chromosomes per condition is 100. Different colors represent different concentrations of LEDGINs added during transduction. (F, H) XY-plot showing the relative number of mapped insertions/Mb (y-axis, log2 scale) over the gene density of each chromosome (x-axis, log2 scale) in SupT1 (F) and Jurkat (H) cells. Thus, each value on the x-axis corresponds to a certain chromosome (see also Supplementary Table S1 for gene densities) and to four y-values, one for each condition. The lines are the result of regression analysis (see also Supplementary Table S2). Two experiments were performed in Jurkat cells and two in SupT1 cells. Results are shown for one representative experiment, referred to as experiment A, in which SupT1 and Jurkat cells were transduced in parallel. GFP; Green Fluorescent Protein, Mb; megabase.